CONSTRUCTION
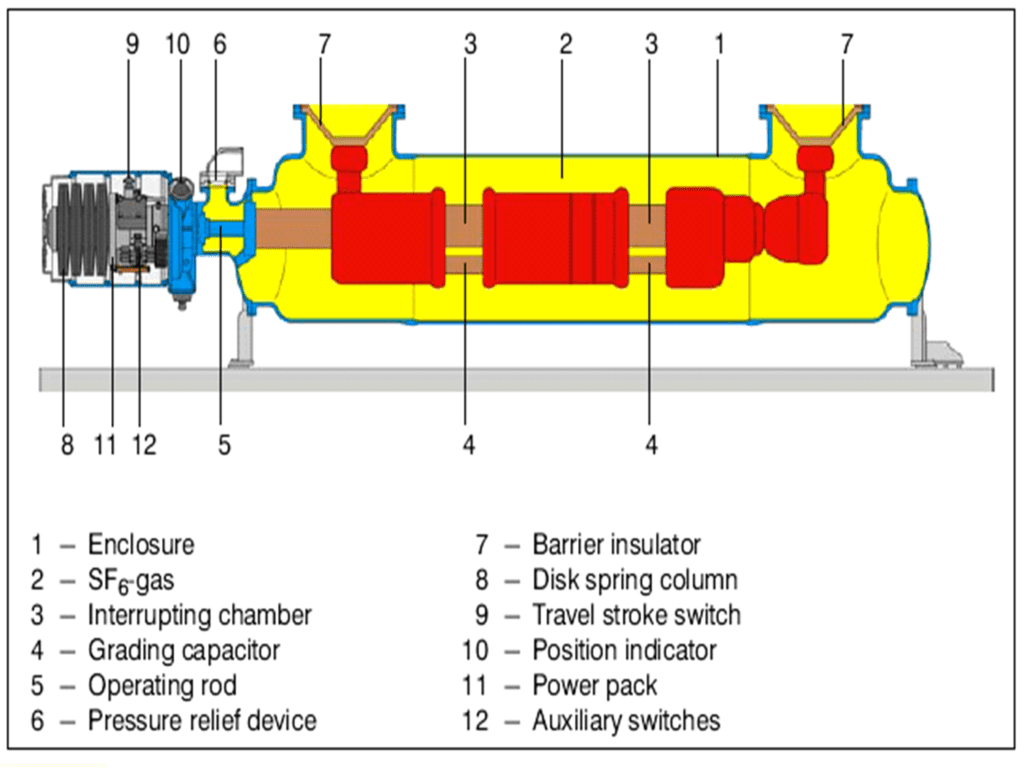
This is basically an aluminum compartment in which the circuit breaker is inbuilt.SF6 gas is to be filled in these compartments after complete installation.
The lower point is the entry point for gas insulated bus and the upper point is the outgoing point of the gas-insulated bus. The lowermost point is for the cable link to local control cabinets to control the relay panel, from where the circuit breaker operation has to be controlled.
The CB is designed and tested according to international standards and fulfills the appropriate requirements

OPERATION OF CB IN GIS
It consists of three vertically arranged self-blast interrupters mounted in a common enclosure and operated by a common spring operating mechanism.
The three-phase circuit breaker unit and support structure form the mechanical basis of the GIS bay.
The CB is applied for any GIS layout e.g. Single busbar and double busbar arrangements.
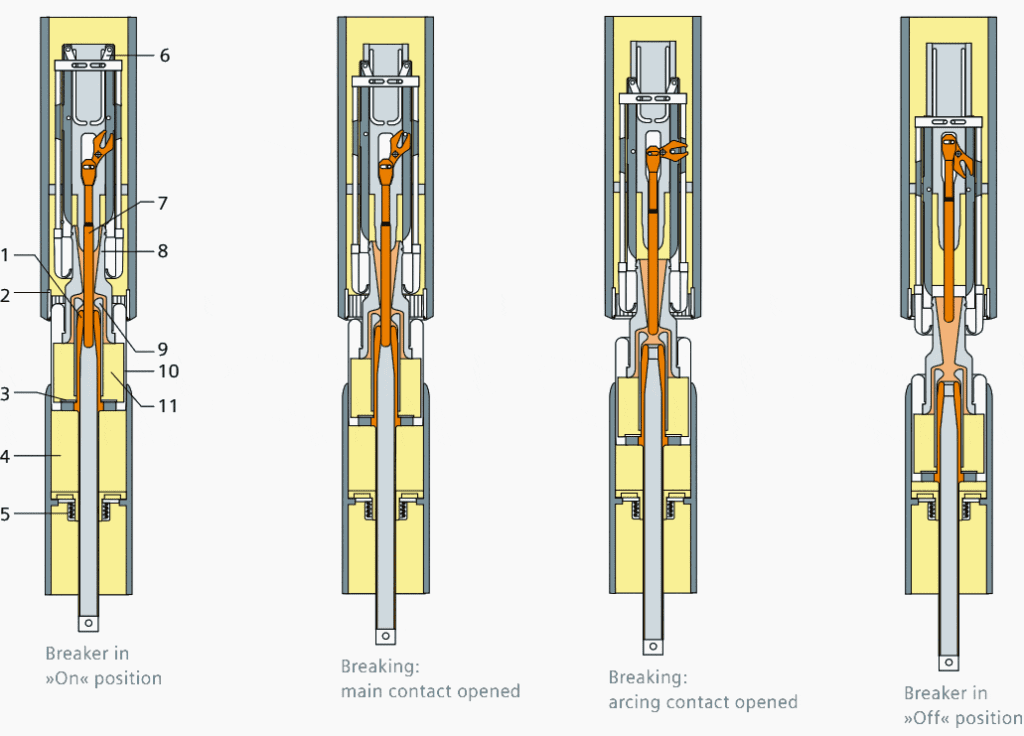
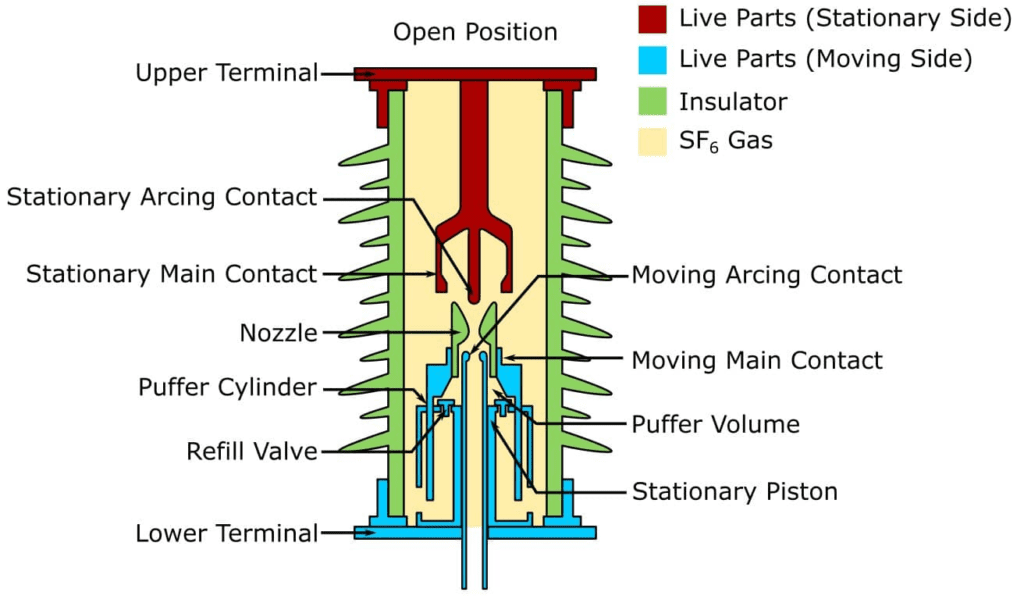
When the interrupter is in the closed position the current flows through the circuit breaker via the outer current-carrying circuit.
When the OPEN command is triggered the blast cylinder starts to leave the contact crown of fixed contact the SF6 gas between the blast cylinder and piston is compressed.
When the arcing contacts are mechanically separated, an arc burns between the moving and fixed arcing contacts.
An intensive blast of SF6 Gas is pressed through the nozzle to extinguish the arc at the next current zero.
- DISTANCE BETWEEN ARCING CONTACTS MUST INCREASE VERY FAST
2. ARC SHOULD QUENCH AT CURRENT ZERO CROSSING WITH BLAST OF SF6.
3.RRDS(RATE OF RISING OF DIELECTRIC STRENGTH) SHOULD BE FASTER THAN RRRV(RATE OF RISING OF RESTRIKING VOLTAGE)DURING ARC QUENCHING
A spring-operated mechanism is one driven by the mechanical energy stored in springs. Typically, the “closing spring” is mechanically charged by a motor and is held in its compressed position by a closing latch.
When a close signal releases this latch, this spring pushes against a mechanical linkage to force the breaker contacts closed and, at once, charges the trip spring. The closing spring is then immediately recharged by the motor. Another latch will hold the tripping spring in the compressed position until an open signal releases this latch

