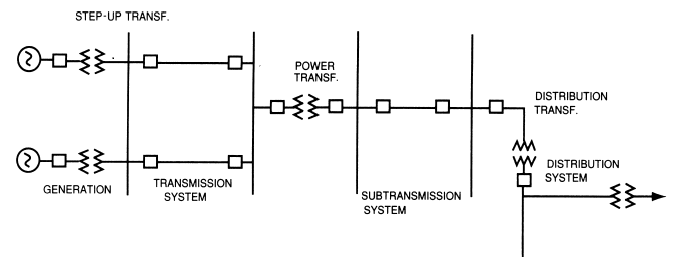
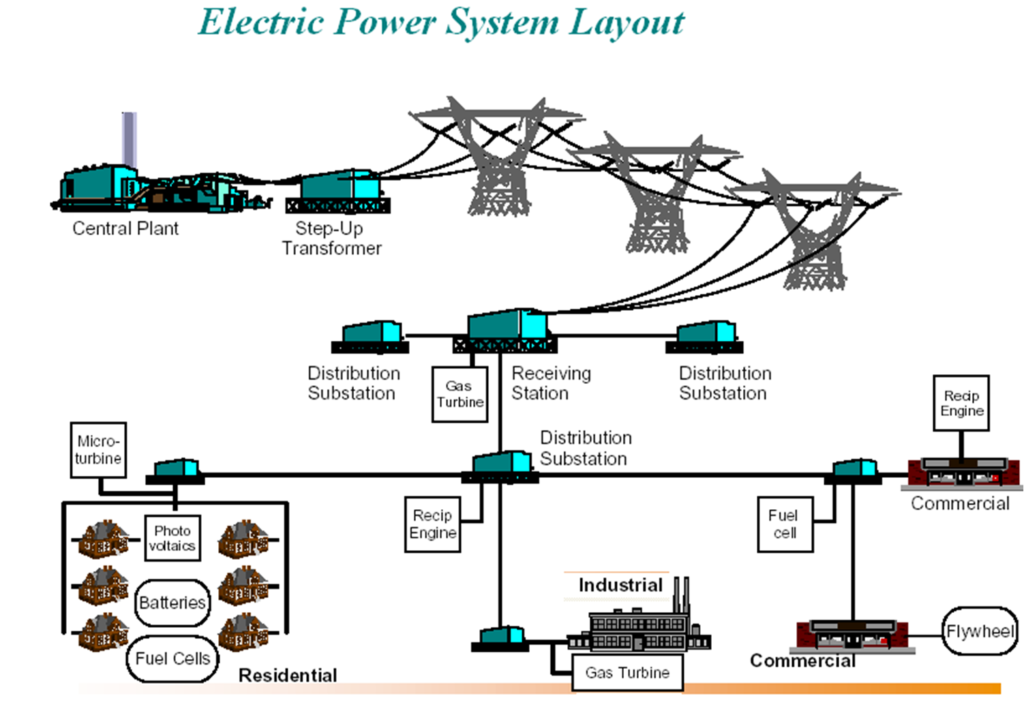
The power system includes all parts of an electric system from power sources to customers.
The Function of the system is to generate power, transmit this power and distribute it to customers at voltage levels and reliability that are appropriate to various users.
VOLTAGE LEVELS
¢Generation: 11kV-25 kV
¢EHV Transmission: 500kV-765kV
¢HV Transmission: 132kV-400kV
¢Distribution system: 415V-33kV
A power plant is an assembly of systems or subsystems to generate electricity, i.e., power with economy and requirements.
TYPES OF POWER GENERATING STATION
- Thermal Power Station
- Nuclear Power Station
- Hydro Power Station
- Renewable Energy Sources
TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
¢High-voltage networks, consisting of transmission lines, connects the power plants and high-voltage substations in parallel.
¢This network permits load sharing among power plants
¢The typical voltage of the network is between 132KV and 765 kV. The high-voltage substations are located near the load centers
ADVANTAGES
Reduces the volume of conductor material.
Increases transmission efficiency
Decreases percentage line drop
DISADVANTAGES
Increased the insulating cost of the conductors
Increased the cost of transformers, switchgear, and other terminal apparatus.
DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
¢The distribution system has two parts, primary and secondary.
¢The primary distribution system consists of overhead lines or underground cables, which are called feeders.
¢The feeders supply the distribution transformers that step the voltage down to the secondary level.
¢The secondary distribution system contains overhead lines or underground cables supplying the consumers directly by single- or three-phase power.
POWER SYSTEM CHALLENGES
¢Power system analysis.
¢Power system planning.
¢Power system control.
¢Power system protection.
¢Power quality.
¢Load management.
¢Distributed generation integration
Objectives of Power System Operators
- To supply Quality Power to the consumer.
- Quality power: Maintaining the frequency and voltage within the limit
- To supply a Reliable and Economical power to the consumer.
Power System Protection
Most of the equipment in the power system is very expensive. To maximize the return from the system, the system must be protected from real-time damages that occur due to faults. In order to prevent loss of life and machinery due to faults various schemes are implemented in all the zones of the power system.
Different Types of power system protection schemes
Different power system protection schemes offer various advantages and disadvantages based on their design, operation, and application. Here are some common power system protection schemes and their associated pros and cons:
- Overcurrent Protection:
- Advantages: Simple and cost-effective, suitable for protecting against overloads and short circuits. Can be applied at various system levels (transmission, distribution, etc.). Offers quick fault detection and clearing.
- Disadvantages: Limited sensitivity to detect faults in some scenarios. Can have coordination challenges when applied at different protection levels. May require coordination with other protective devices for selectivity.
- Distance Protection:
- Advantages: Provides good selectivity and high-speed fault detection. Well-suited for transmission line protection. Offers zone coverage, enabling identification of fault locations. Can handle system changes and dynamic conditions.
- Disadvantages: Complex implementation and settings. Requires accurate line impedance data. Susceptible to errors due to changes in line parameters or system configuration.
- Differential Protection:
- Advantages: Highly sensitive and selective, suitable for protecting transformers, generators, and motors. Detects internal faults irrespective of fault location. Can provide fast and reliable fault detection.
- Disadvantages: Requires current transformers (CTs) and voltage transformers (VTs) for proper operation. Challenging to coordinate and set for complex power system configurations. Costlier and more complex than other protection schemes.
- Impedance Protection:
- Advantages: Provides high-speed fault detection and selectivity. Can be applied for both transmission lines and distribution feeders. Resistant to CT saturation and external faults. Allows for distance-to-fault estimation.
- Disadvantages: Requires accurate knowledge of the system impedance characteristics. Sensitive to changes in system parameters and fault resistance. Complex coordination with other protection devices.
- Differential and Restricted Earth Fault (REF) Protection:
- Advantages: Effective for protecting transformers against internal and external faults. Offers fast and selective fault detection. REF protection enhances sensitivity for ground faults.
- Disadvantages: Requires CTs and VTs for proper operation. Coordination challenges when protecting transformers with various winding configurations. May be sensitive to CT saturation and inrush currents.
- Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection:
- Advantages: Monitors system voltage levels and provides protection against abnormal voltage conditions. Helps prevent equipment damage and ensure system stability. Can trigger load shedding or automatic voltage control.
- Disadvantages: Requires accurate voltage measurement. Challenging to set appropriate thresholds for different system conditions. Limited effectiveness against certain fault types.
- Frequency Protection:
- Advantages: Monitors system frequency and provides protection against abnormal frequency conditions. Helps prevent equipment damage and system instability. Can trigger load shedding or automatic frequency control.
- Disadvantages: Requires accurate frequency measurement. Challenging to set appropriate thresholds for different system conditions. Limited effectiveness against certain fault types.
It’s important to note that the selection and deployment of protection schemes depend on the specific requirements, system characteristics, and operational needs of the power system. A comprehensive and coordinated protection strategy often involves a combination of these schemes to ensure reliable and efficient power system operation.

