Classified into three broad categories based on the excitation power source:
•DC excitation systems
•AC excitation systems
Static excitation systems
1. DC Excitation Systems:
•It utilizes dc generators as a source of power; driven by a motor or the shaft of the main generator;
self or separately excited
•represent early systems (1920s to 1960s);
lost favor in the mid-1960s because of large size; superseded by ac exciters
•voltage regulators range from the early non-continuous rheostatic type to the later system using magnetic rotating amplifiers
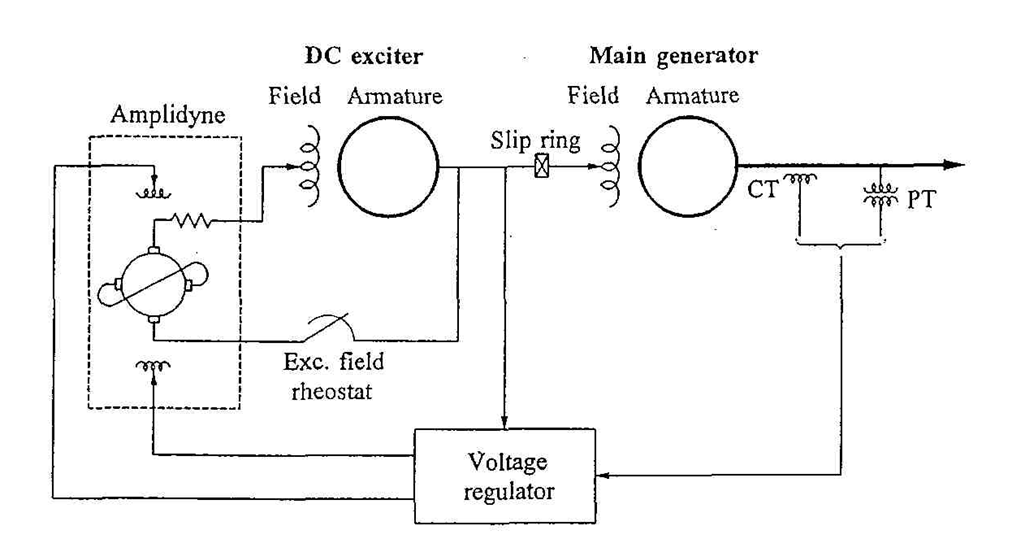
•self-excited dc exciter supplies current to the main generator field through slip rings
•exciter field controlled by an amplidyne which provides incremental changes to the field in a buck-boost scheme the exciter output provides the rest of its own field by self-excitation
2. AC Excitation Systems:
•use ac machines (alternators) as a source of power
•usually, the exciter is on the same shaft as the turbine-generator
•the ac output of the exciter is rectified by either controlled or non-controlled rectifiers
•rectifiers may be stationary or rotating
•early systems used a combination of magnetic and rotating amplifiers as regulators; most new systems use electronic amplifier regulators
2.1 Stationary rectifier systems:
•dc output to the main generator field supplied through slip rings
•when non-controlled rectifiers are used, the regulator controls the field of the ac exciter;
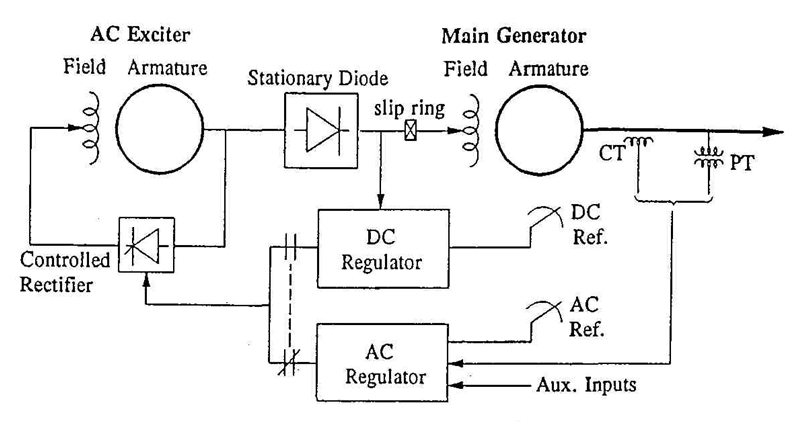
When controlled rectifiers are used, the regulator directly controls the dc output voltage of the exciter
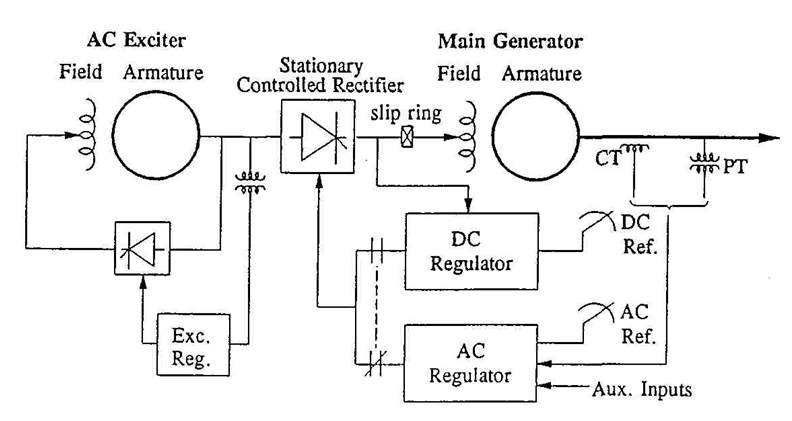
2.2 Rotating rectifier systems:
•the need for slip rings and brushes is eliminated; such systems are called brushless excitation systems
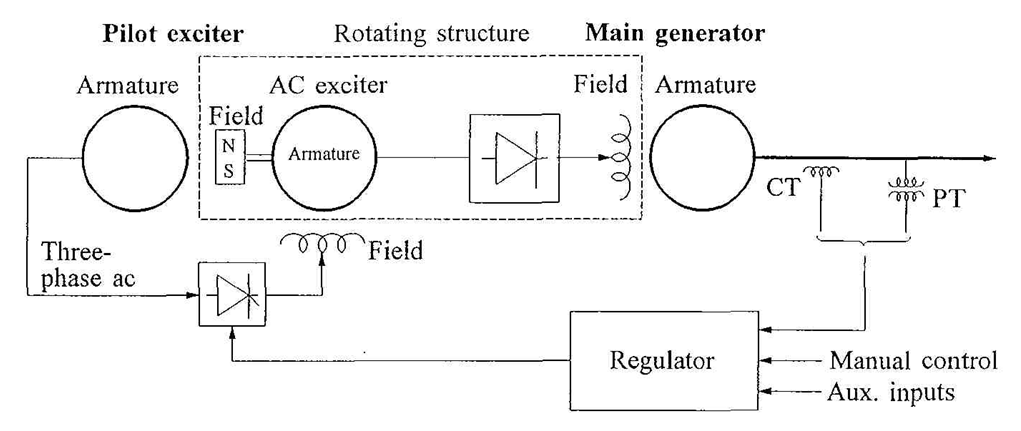
•they were developed to avoid problems with the use of brushes perceived to exist when supplying the high field currents of large generators
•they do not allow direct measurement of generator field current or voltage
3. Static Excitation Systems:
•all components are static or stationary
•supply dc directly to the field of the main generator through slip rings
the power supply to the rectifiers is from the main generator or the station auxiliary bus
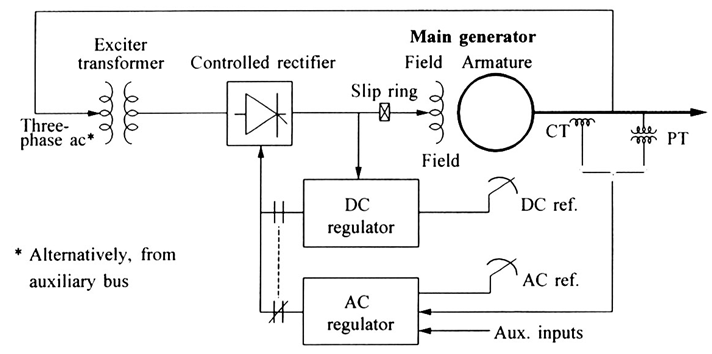
3.1 Potential-source controlled rectifier system:
•excitation power is supplied through a transformer from the main generator terminals
•regulated by a controlled rectifier
•commonly known as bus-fed or transformer-fed static excitation system
•very small inherent time constant
•maximum exciter output voltage is dependent on input ac voltage; during system faults the available ceiling voltage is reduced
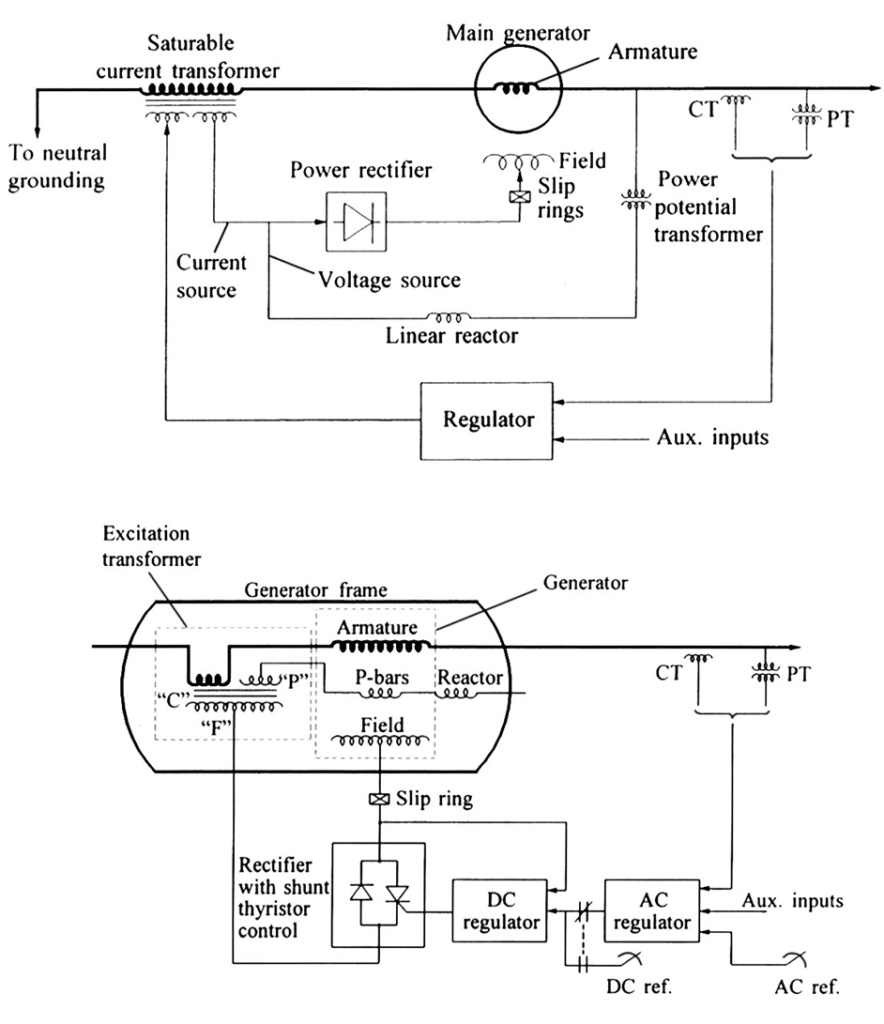
3.2 Compound-source rectifier system:
•power to the exciter is formed by utilizing the current as well as the voltage of the main generator
•achieved through a power potential transformer (PPT) and a saturable current transformer (SCT)
•the regulator controls the exciter output through controlled saturation of the excitation transformer
•during a system fault, with depressed generator voltage, the current input enables the exciter to provide high field forcing capability
3.3 Compound-controlled rectifier system:
•utilizes controlled rectifiers in the exciter output circuits and the compounding of voltage and current within the generator stator
•result is a high initial response static system with full “fault-on” forcing capability


1 Comment
Pingback: Functions and Performance Requirements of Excitation Systems - Learn With Electric Know How