Objectives
- Define distribution line faults and their significance in electrical distribution systems.
- Understand the impact of faults on system reliability, safety, and service interruptions.
Fault analysis is conducted by DISCOM Engineers for the following purposes
- Locate faults
- Know the cause,
- Determine if protective equipment is operated properly,
- Methods to implement in order to prevent the fault from occurring in the future
Faults are abnormal states of the distribution network, usually associated with open circuits or short circuits or insulation breakdown between two or more points.It can be either temporary or permanent.
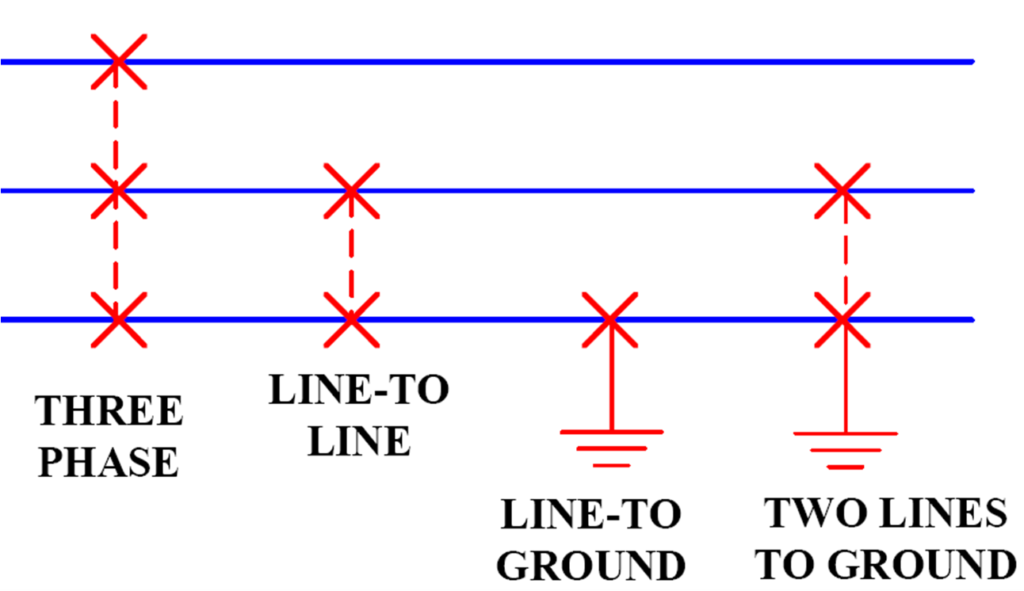
The temporary faults include the insulation breakdown by the interaction between the components and external agents (lightning strikes, wind, transient tree contacts, etc.) for a short period of time.
Examples of permanent faults are insulator damage by flashover, underground cable breakdown, and surge arrester damage.
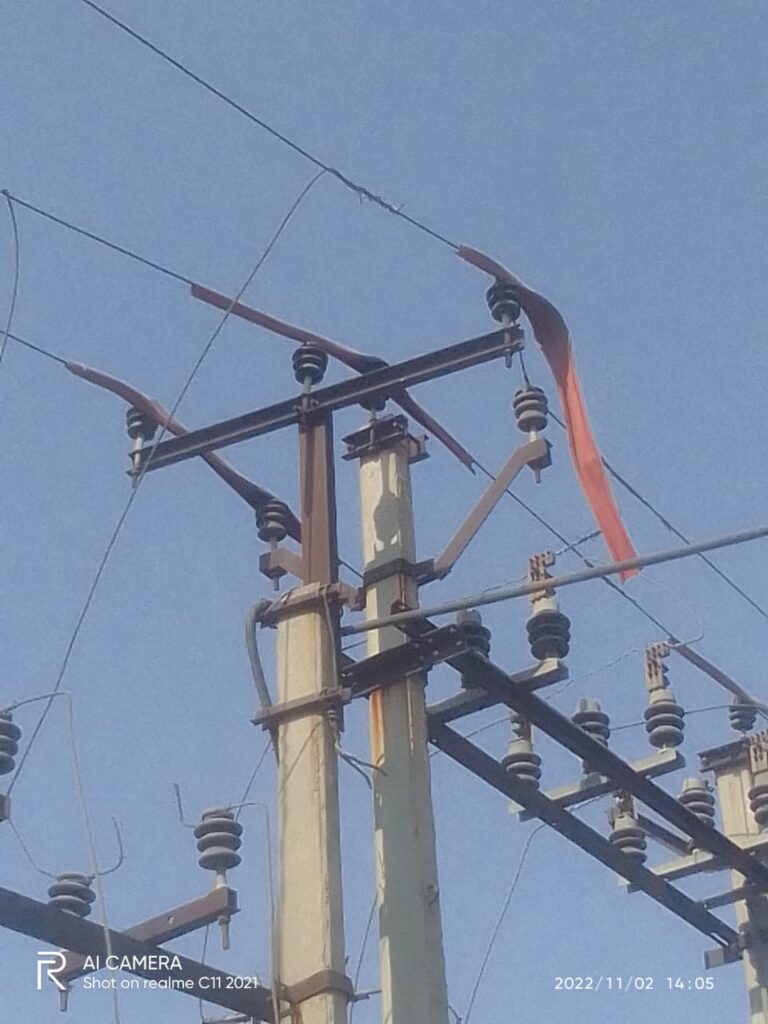
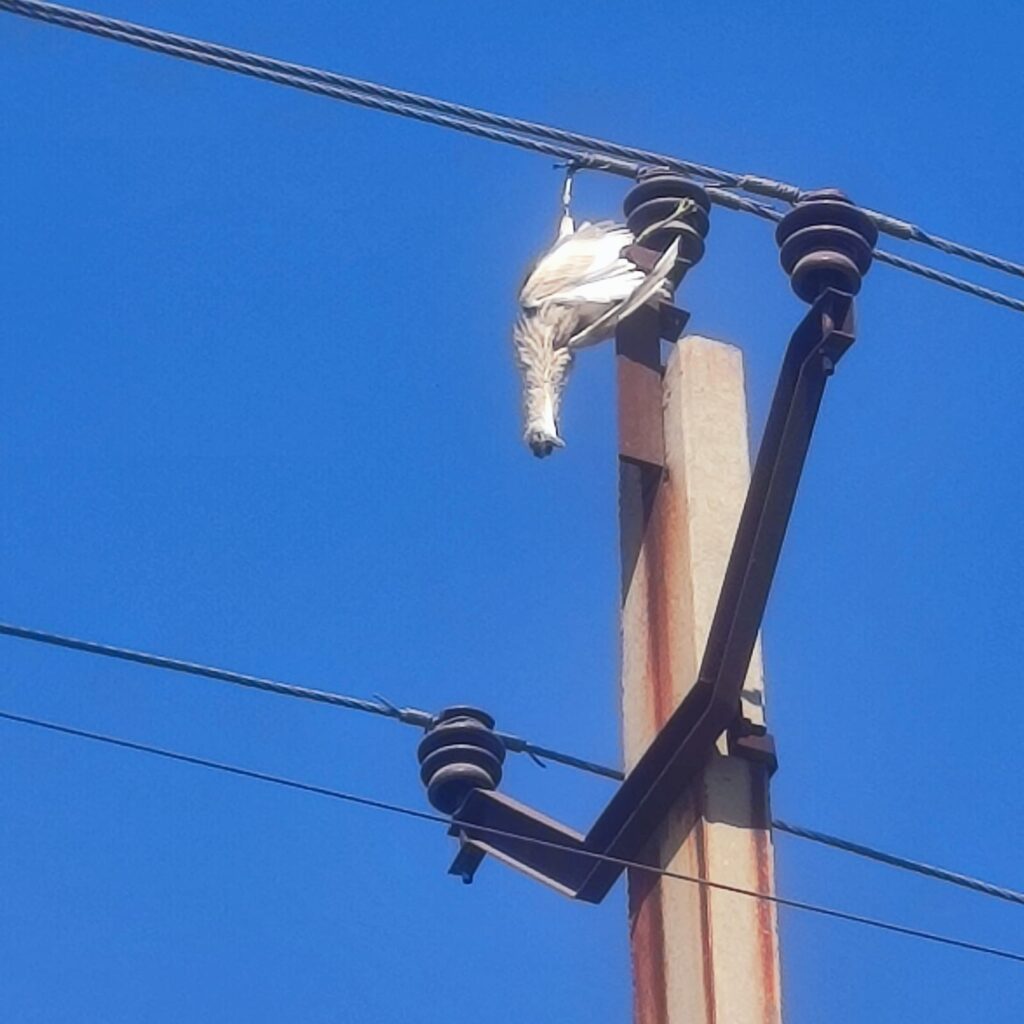
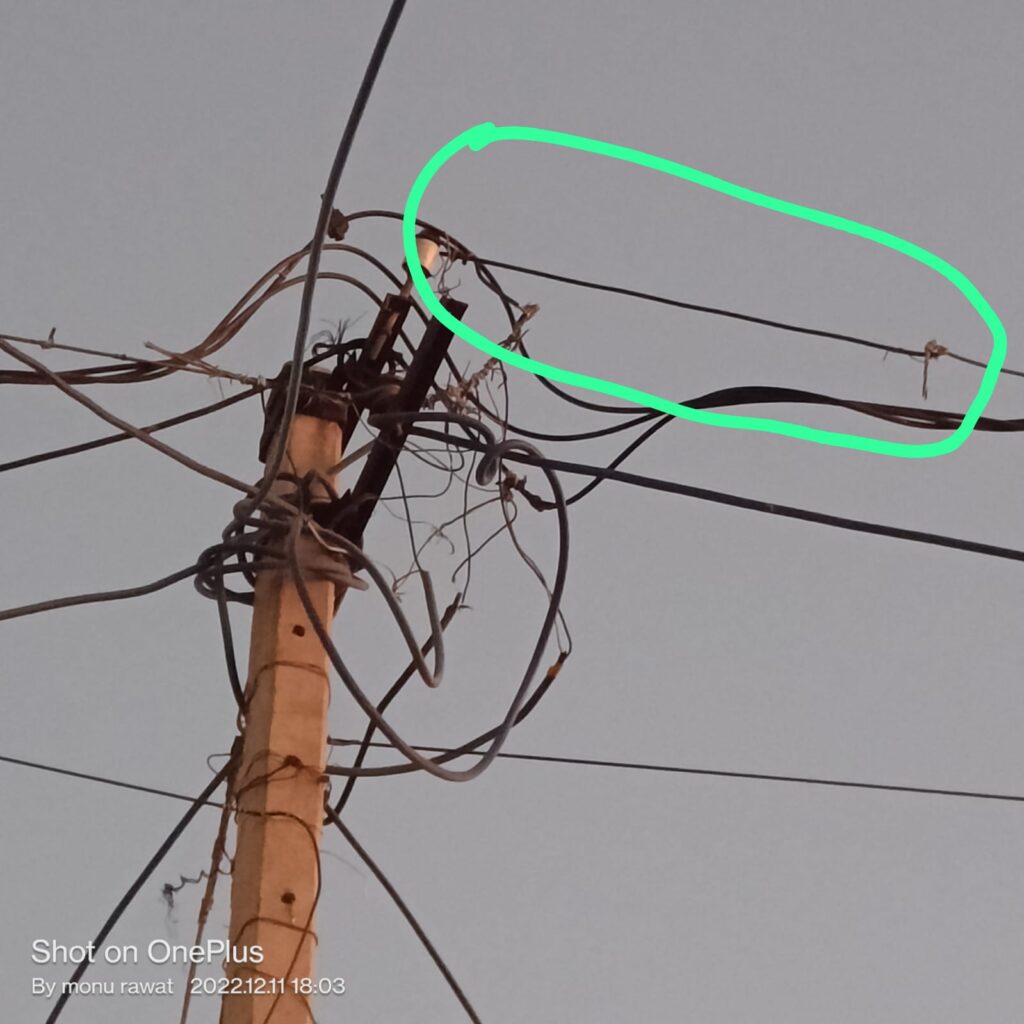



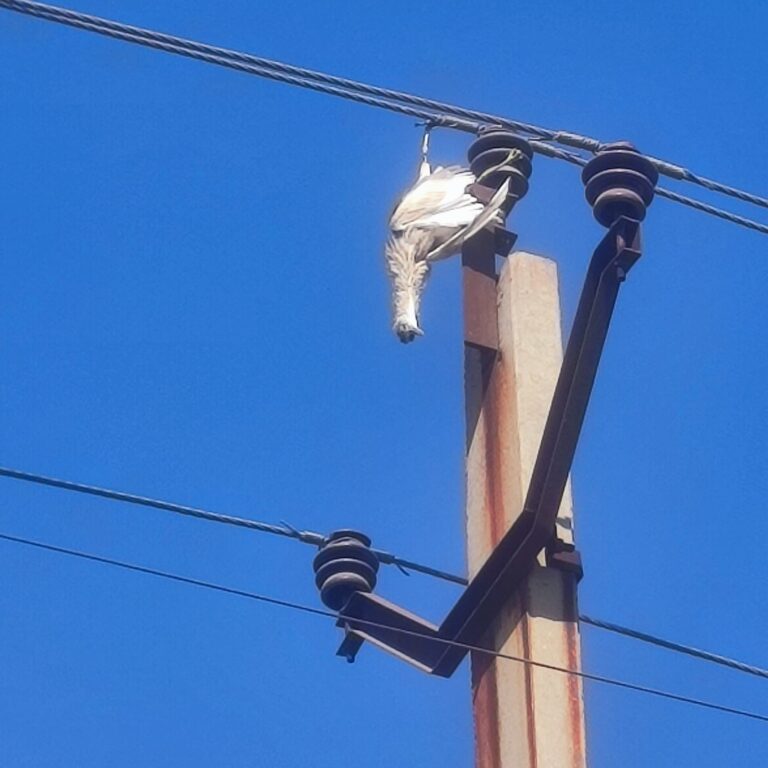
| FAULTS IN OVERHEAD DISTRIBUTION LINE | FAULTS IN UG CABLE | |
| OCCURRENCE | Frequent | Rare |
| CAUSES | Extreme Weather Conditions, Tree Branches, Bird Faults, construction, and vehicle, Insulation Puncture, Conductor Snapping | excavator digging, Partial Discharge |
| Fault Rectification | Less time compared to UG Cable | More time |
Effect of Fault
- Danger to Operating Personnel
- Loss of Equipment
- Disturbance in the Interconnected Active Circuits
- Electrical Fire
Protection in Distribution Network
If we are able to disrupt or break the circuit when a fault occurs, it reduces the considerable damage to the equipment and the system.
fault-limiting devices
fuses, circuit breakers, and relays
Fault detection in distribution lines is a critical aspect of maintaining a reliable and efficient electrical power distribution system. Electrical faults can lead to disruptions, equipment damage, safety hazards, and downtime. Detecting faults quickly and accurately is essential for minimizing these negative impacts. Several methods and technologies are employed for fault detection in distribution lines:
I hope that you got to know about the different types of faults in distribution systems. Thank you for your valuable time spent on the article. Furthermore, please write your feedback in the comment section below related to the power system.


