📘 Introduction
The efficiency and safety of an electrical distribution system greatly depend on the type of cables used. Depending on environmental conditions, voltage levels, and load demands, engineers choose from various cable types—most commonly XLPE, PILC, and Aerial Bundled Cables (ABC).
This article provides a comparative overview of these key distribution cable types, their construction, performance, advantages, and typical applications.
🔌 1. XLPE Cables (Cross-Linked Polyethylene)
🔍 Overview
XLPE cables use cross-linked polyethylene as the insulation material. This thermoset material enhances heat and chemical resistance.
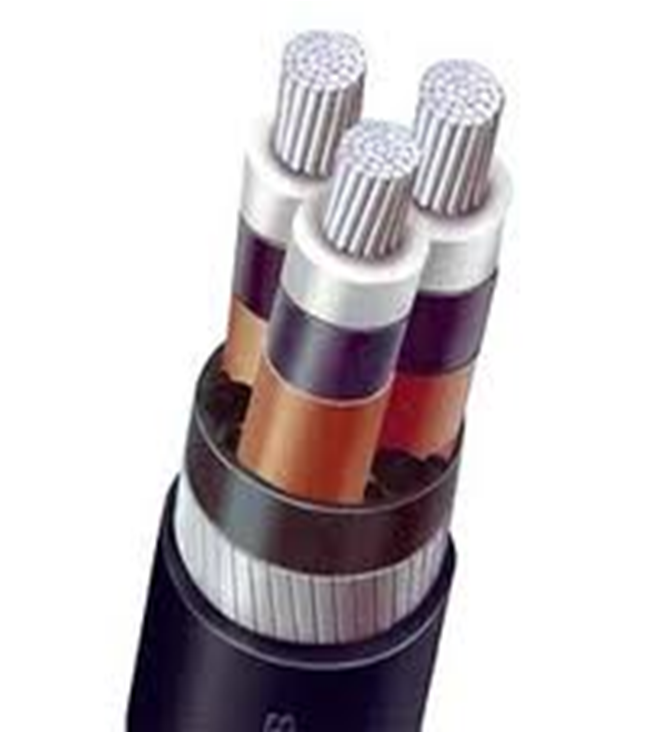

🔧 Construction:
- Conductor (usually aluminium or copper)
- XLPE insulation
- Metallic screen (optional)
- Outer PVC or HDPE sheath
📈 Features:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | LV to 66 kV and beyond |
| Temp. Withstand | Up to 90–105°C (continuous) |
| Flexibility | High |
| Moisture Resistance | Good |
✅ Advantages:
- High thermal rating and ampacity
- Lightweight and easy to install
- Low dielectric losses
- Good resistance to chemicals and water
➖ Disadvantages:
- Sensitive to mechanical damage if not armored
- Costlier than PILC for the same rating
📌 Applications:
- Underground feeders
- Industrial installations
- Urban distribution systems
🧪 2. PILC Cables (Paper-Insulated, Lead-Covered)
🔍 Overview
PILC cables are traditional underground cables using impregnated paper insulation and lead sheathing. Although gradually phased out, they are still present in older grids.
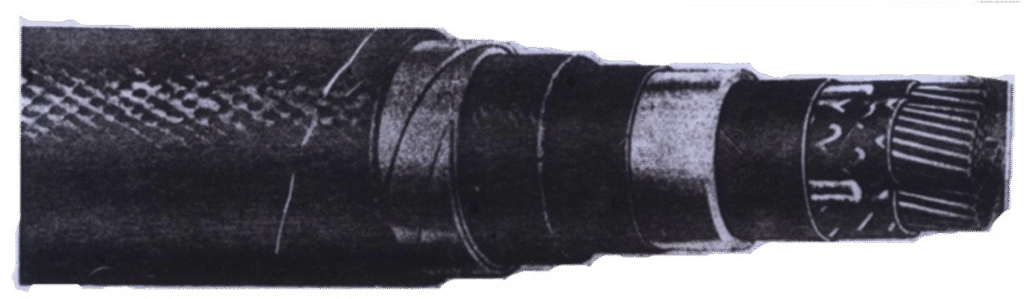
🔧 Construction:
- Copper conductor
- Layers of oil-impregnated paper
- Lead sheath for waterproofing
- Steel tape armor (optional)
- Bitumen or jute outer layer
📈 Features:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | Typically up to 33 kV |
| Temperature Rating | ~70°C |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent (due to lead sheath) |
✅ Advantages:
- Long service life in buried installations
- Robust against water ingress
- High mechanical protection (with armor)
➖ Disadvantages:
- Heavy and difficult to handle
- Environmentally hazardous due to lead
- Prone to aging and insulation failure over time
- Maintenance-intensive
📌 Applications:
- Legacy underground networks
- Special cases where replacement is cost-prohibitive
⚡ 3. Aerial Bundled Cables (ABC)
🔍 Overview
ABC consists of multiple insulated conductors twisted together and suspended overhead—an alternative to bare conductors in LT/HT overhead systems.
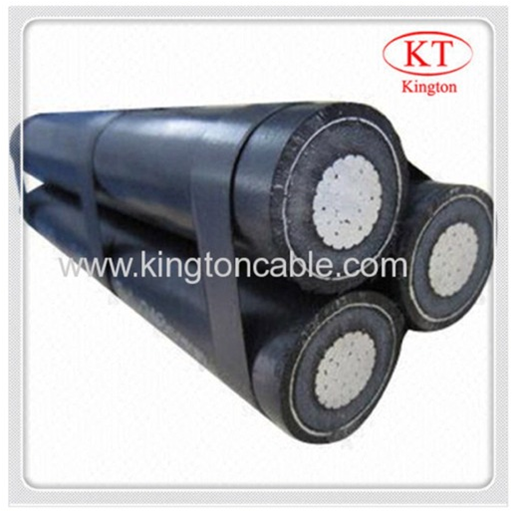

🔧 Construction:
- Phase conductors (aluminium, XLPE insulated)
- Neutral messenger (bearer wire)
- UV-protected outer sheath
📈 Features:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | LV (415 V) to MV (11–33 kV) |
| Installation | Overhead, with poles |
| Insulation | XLPE or HDPE |
✅ Advantages:
- Reduced risk of electrocution and outages
- Suitable for congested urban/rural areas
- Improved theft resistance
- Lower line losses and fewer faults due to insulation
➖ Disadvantages:
- Requires tensioning and proper pole design
- Heat buildup under full load if improperly sized
- Not suitable for high-power feeders
📌 Applications:
- Urban slums and rural electrification
- Forest or hilly terrain
- Street lighting and temporary connections
🧮 Comparison Table
| Feature | XLPE | PILC | ABC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation | Underground | Underground | Overhead |
| Flexibility | High | Low | Medium |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 105°C | ~70°C | ~90°C |
| Environmental Impact | Low | High (due to lead) | Low |
| Maintenance | Low | High | Moderate |
| Theft Resistance | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Cost (Initial) | Medium–High | High | Low–Medium |
| Lifespan | ~30–40 years | 40+ (if intact) | ~25–30 years |
🧰 Guidelines ON CABLE LAYING

- Use XLPE for underground, high-load, and high-reliability applications.
- Retain PILC only in legacy networks where retrofit is uneconomical.
- Deploy ABC where safety, space constraints, or theft prevention are key concerns.
- A power cable should not be bent less than 8 times of it’s overall dia.(I.S.1026-1966)
- A power cable must maintain a minimum distance of 0.4 meter with a water supply line. (both running parallel and crossing).
- DEPTH OF CABLE LAYING
- UP to 1.1 Kv- 0.45 meters
- 3.3.Kv to 11Kv- 0.75 meters
- 22Kv to33Kv- 1.0 meter
- To reduce mutual heating and one faulty cable cause injury to a healthy one preferably spacing of 0.4 meters to be maintained. In worst case it should not be less than 0.25 meters.
- POWER CABLE CROSSING HIGH WAY -Power cables should be laid under the roads through a cast iron or steel pipe at an angle to prevent a sharp angle at the point of entry and less loading factor.
📌 Conclusion
Each cable type—XLPE, PILC, and ABC—has a unique role in distribution systems depending on cost, environment, and performance needs. Understanding their characteristics helps engineers design systems that are reliable, cost-effective, and safe.

