📘 Introduction
The electrical distribution network is susceptible to faults such as short circuits, overcurrents, and ground faults. To protect equipment and maintain service continuity, protection systems are used to detect and isolate these faults quickly and efficiently.
This article provides a clear understanding of distribution protection components—specifically fuses, relays, and reclosers—highlighting their functions, types, advantages, and how they coordinate within the system.
🔐 Why Protection Is Essential in Distribution Systems
- Safety of personnel and the public
- Prevent equipment damage (transformers, lines, etc.)
- Minimize outages and downtime
- Improve system reliability
- Ensure selective isolation of only the faulty section
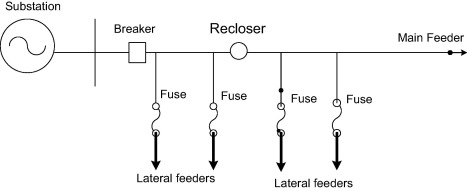
🔌 1. Fuses in Distribution Systems
🔍 What is a Fuse?
A fuse is a simple protective device that interrupts excessive current by melting a fusible link.

✅ Key Features:
- One-time use (non-resettable)
- Passive protection (no sensing/control mechanism)
- Fast-acting and cost-effective
📂 Types of Fuses:
| Type | Application |
|---|---|
| Drop-out Fuse | Pole-mounted transformers/feeders |
| Cartridge Fuse | Indoor panel boards and control systems |
| Expulsion Fuse | Medium-voltage outdoor lines |
➕ Advantages:
- Inexpensive
- Simple installation
- Good for rural and remote areas
➖ Limitations:
- Must be replaced after the operation
- No remote control or indication
- No coordination for temporary faults
⚙️ 2. Protective Relays
🔍 What is a Relay?
A protective relay is an intelligent device that monitors electrical parameters and sends a signal to a circuit breaker during abnormal conditions.
🧠 Functions:
- Detects overcurrent, earth fault, undervoltage, reverse power, etc.
- Sends trip signal to breaker
- Provides fault logging and alarms
📂 Types of Relays:
| Relay Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Overcurrent Relay | Trips on overload or short-circuit current |
| Earth Fault Relay | Detects current to ground (leakage) |
| Differential Relay | Compares input/output current of a transformer |
| Numerical Relay | Digital, programmable, with communication |
➕ Advantages:
- Precise and programmable
- Enables selective tripping
- Works with SCADA and automation systems
➖ Limitations:
- Requires auxiliary power
- Complex setup and calibration
- Higher cost than fuses
🔄 3. Reclosers
🔍 What is a Recloser?
A recloser is an automatic switchgear device that detects faults, interrupts the circuit, and then automatically recloses after a short time.
🧠 Functionality:
- Ideal for temporary faults (e.g., lightning, tree branches)
- Can be programmed for multiple reclose attempts (e.g., 3 shots to lockout)
- Operates as a breaker with intelligence
📂 Types of Reclosers:
| Type | Voltage Range | Operation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Recloser | Up to 15 kV | Self-powered |
| Electronic Recloser | 11–38 kV | Microprocessor-controlled |
➕ Advantages:
- Restores power automatically
- Reduces manual intervention
➖ Limitations:
- Higher initial cost
- Requires maintenance and programming
- Misoperations are possible if not coordinated well
🔗 Coordination of Protection Devices
| Device | Role in Coordination |
|---|---|
| Fuses | Provide backup or local isolation |
| Relays | Selectively trip downstream faults |
| Reclosers | Isolate temporary faults and restore supply |
🔄 Fuse–Recloser Coordination: Fuses are usually placed downstream of reclosers. Reclosers attempt to clear temporary faults before fuses operate.
🛡️ Relay–Recloser Coordination: In urban networks, relays and reclosers must be set with time-current curves to ensure selective tripping.
🧰 Best Practices for Distribution Protection
- Use graded protection (fuse–relay, breaker hierarchy)
- Regularly test and calibrate relays and reclosers
- Ensure clear discrimination settings between upstream and downstream devices
- Integrate with SCADA for real-time monitoring
- Implement auto-reclose logic only where safe and effective
📌 Conclusion
An efficient distribution protection system relies on the strategic use of fuses, relays, and reclosers. Each has its specific role—fuses for simplicity, relays for intelligence, and reclosers for continuity. Proper selection and coordination ensure the safety, reliability, and resilience of the power distribution network.

