Objectives
- Introduction to power system protection
- Understand the need for the protection of electric equipment and their protection schemes
- Understand Generator Protection, Transformer Protection, Transmission line protection
- Understand the operations of various types of circuit breakers and their ratings
- Contribute to the system reliability improvement
Why Protection is needed?
Protection schemes are designed to detect and mitigate electrical faults, preventing damage to equipment and ensuring system reliability. These schemes rely on protective relays and devices to respond to abnormal conditions.
•Small disturbances
–The control system can handle these
–Example: variation in transformer or generator load
•Severe disturbances require a protection system
–They can jeopardize the entire power system
–They cannot be overcome by a control system
Principles and elements of the protection system
We need to balance reliability and cost in designing a power system. While it is impossible to avoid the occurrence of faults and other abnormal operating conditions that produce large power system disturbances, a protection system is intended to take preventive or corrective actions in such cases.
The first line of defense is the protection of power system elements. The function of this type of protection is to detect faults and abnormal conditions and to disconnect the faulted element in order to prevent further damage to the element or a system disturbance. Modern power systems operate near the security limits. The system also needs protection functions at the system level that can include low frequency or low voltage load shedding among others.
Protection operation disconnects system elements. It is then important to provide automatic restoration functions. Among these functions, we might mention the automatic reclosing of transmission lines, automatic transfer to alternate power supplies, and automatic synchronization.
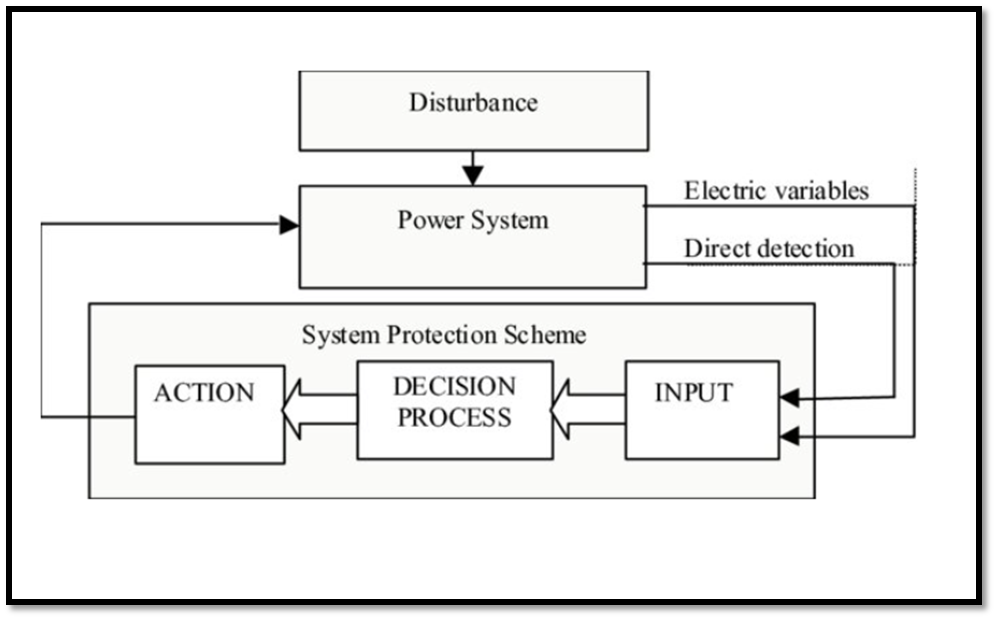
Protection System
A series of devices whose main purpose is to protect persons and primary electric power equipment from the effects of faults
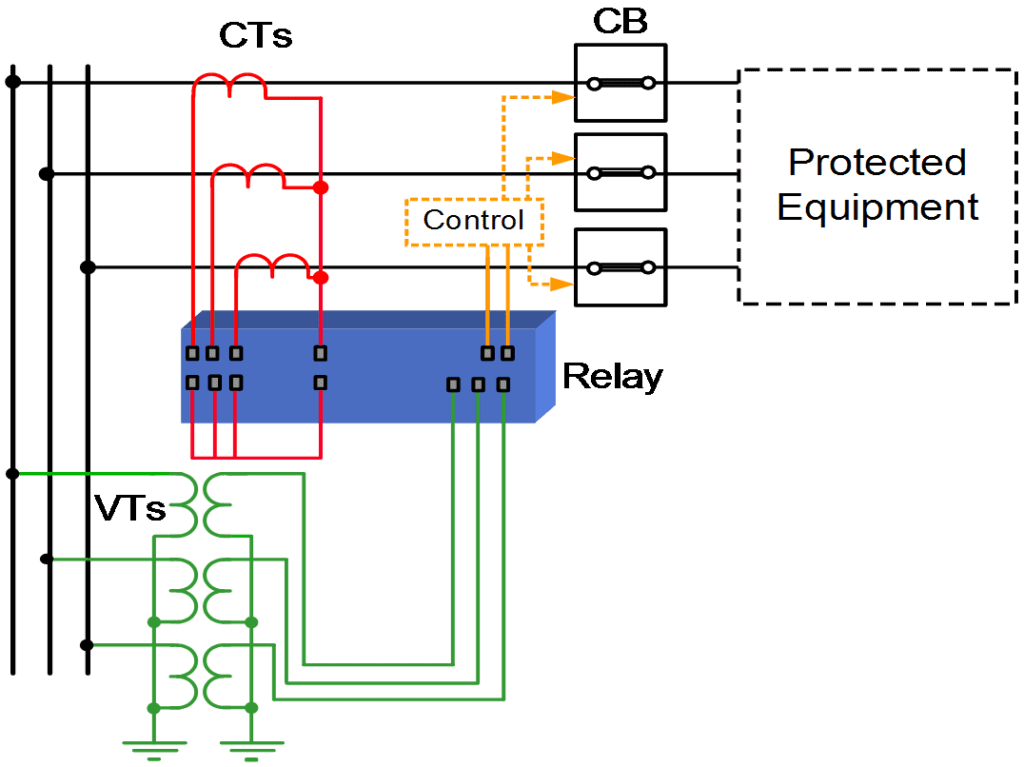
Elements of Protection System
•Current and voltage transducers
Performance Requirements of Protection System
Discriminate between load (normal) and fault (abnormal) conditions
Not be confused by non-damaging transient conditions
Be selective – coordinate with other protection systems
Fast enough to prevent damage and hazards – but not too fast
Have no “blind spots” i.e. unprotected zones
A high degree of reliability and availability
Secure against incorrect operation (security)
Should not restrict rating of primary plant and equipment
Should be affordable
Summary
Engineers and technicians must have a thorough knowledge of these concepts to design, install, and maintain robust protection systems that safeguard equipment and prevent power disruptions.