INTRODUCTION
We have a good idea about substations, they are used for controlling, switching, protection, and step-up or step-down voltages purposes for the T&D of electric energy. We have Air insulated and Gas insulated substations in general.
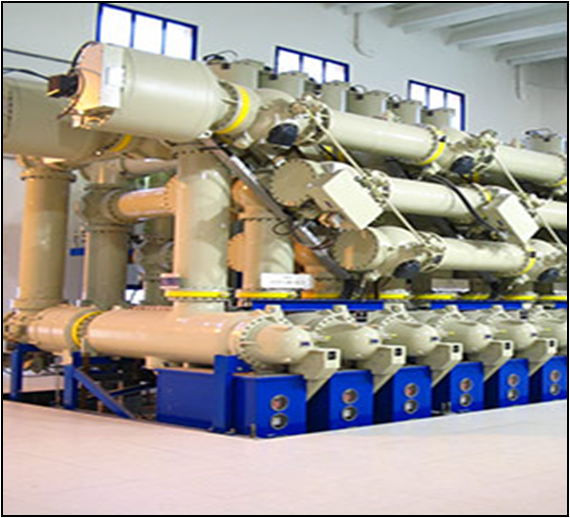
A Gas Insulated Substation (GIS) is a high-voltage substation in which the major electrical equipment is contained in a sealed environment with sulfur hexafluoride gas as the insulating medium. GIS technology offers several advantages over traditional air-insulated substations (AIS) in terms of compactness, reliability, and safety.
Background
Japan introduced Gas insulated Substation technology. Its research and development studies started in 1963 and the first GIS was of 84 kV value in 1968. After that, they introduced 550kV in 1973.
Insulation material: We desire a substation of compact size and for insulation in GIS we used SF-6 Gas (Sulphur Hexa-fluoride Gas) over air used in air insulated substation. Because the insulating property of SF-6 is 2 to 3 times is more than air at a specific pressure.
Advantages of GIS:
•Clearances for GIS, roughly a tenth of that for AIS
•With GIS technology, the clearance needed for phase-to-phase or phase-to-ground for all equipment is much less than that of an AIS or air-insulated substation.
•The total space required for a GIS is roughly a tenth of that needed for a conventional AIS facility. While the conventional, AIS requires several feet of air insulation to isolate a conductor, SF6 gas insulation only needs inches, allowing a GIS facility to fit into areas far smaller than that of an AIS facility. A GIS is mainly constructed where real estate space is expensive or scarce.
- Used for environment sensitive-
•GIS technology is a good choice to use in arctic or desert locations, as it can be enclosed in a building that is environmentally protected from extreme conditions.
•In addition to protecting the system components from extreme heat and cold, GIS technology encloses the electrical components within a Faraday cage which shields the system from potential lightning strikes.
Disadvantages of GIS Systems
GIS equipment tends to have a higher initial cost compared to AIS.
• Delivery of SF6 gas to the site can be problematic.
• GIS substations are indoor type, requiring a separate building.
• System cleaning/maintenance is critical to reducing conductive particle contamination.
• Particle or moisture contamination inside the compartment causes flashovers.
• Outages can be extremely long, and the damage to the system will normally be severe following a fault condition at a GIS substation.
• Access to live parts for maintenance is more problematic and harder to diagnose without gas reclamation and disassembly of the modules.
Types of Equipment Modules in GIS
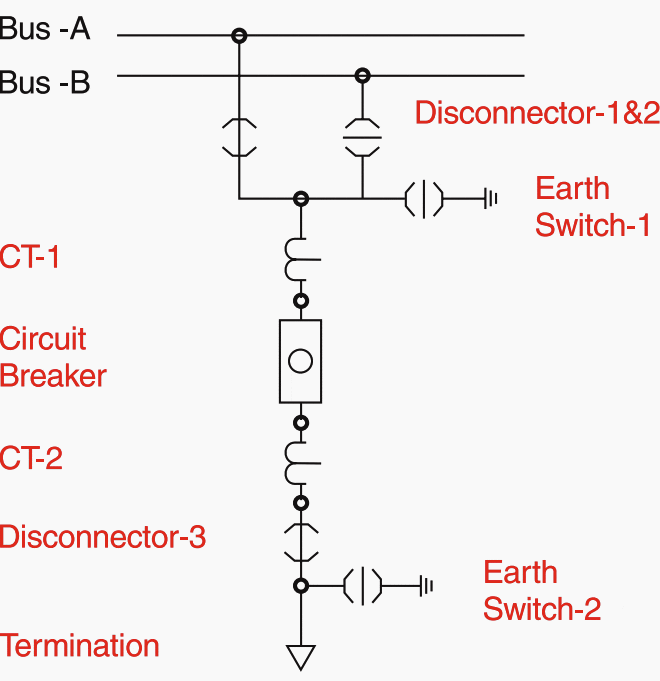
Modular Design:
GIS equipment is often designed in modular units, making it easier to expand or upgrade substations as needed. This modularity also simplifies transportation and installation.
Types of modules include:
• current transformers
• voltage transformers
• Disconnector switches and ground switches
• interconnecting bus
• surge arresters
• Cable connections to the rest of the electric power system
local control cubicle
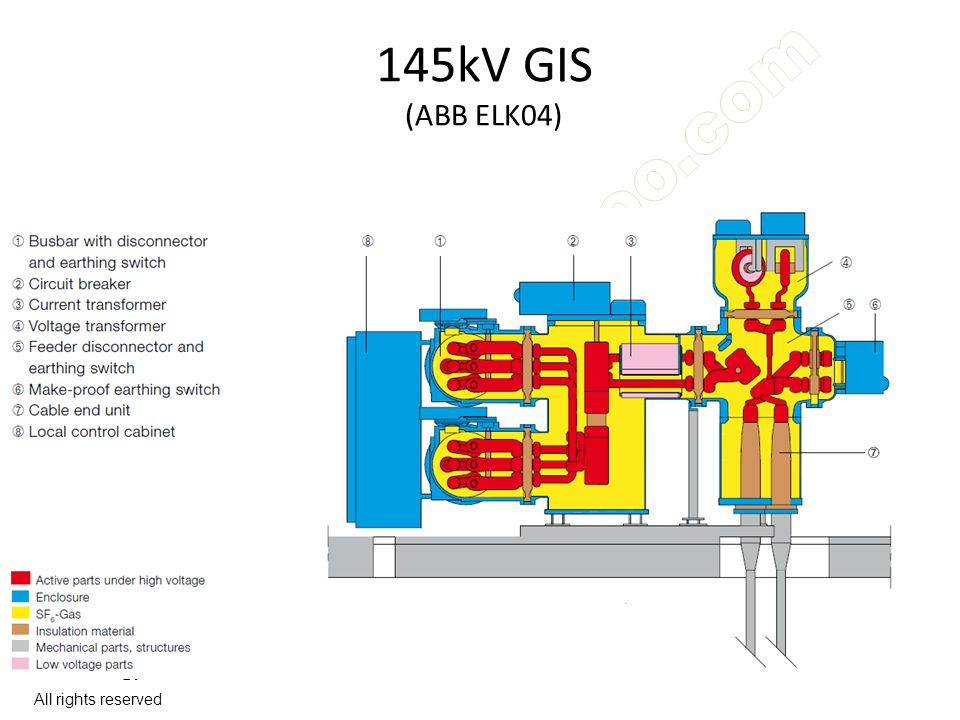
Gas Insulated Substations have become increasingly popular in modern electrical infrastructure due to their numerous advantages, especially in densely populated areas where space is limited, and reliability is crucial. However, ongoing research and development are focused on addressing the environmental concerns associated with SF6 gas and finding more sustainable alternatives.


