D.C. Supply in a Power Station or Sub-Station is very essential as all most the protection and control system work on it allso at the time of A.C. failure, D.C. supply is utilized for emergency lighting.
There are two sets of batteries for every 110 nos. of cells. Per each set, a provision is there for connecting either a boost charger or a float charger to the batteries for charging.
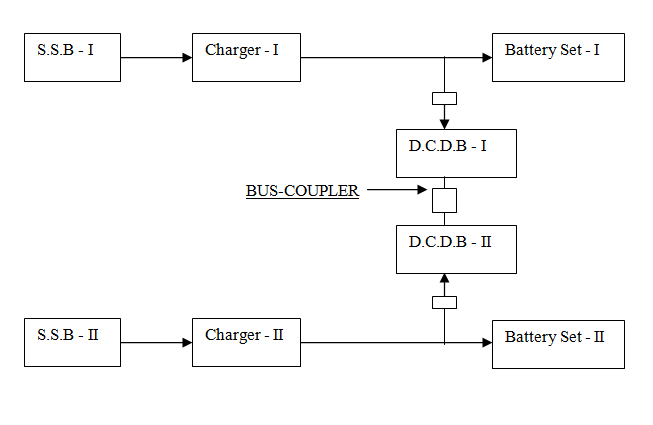
Batteries and D.C.D.B.S which are in parallel to each other are normally kept charged from the respective trickle charger.
On this condition the D.C. load of the Station is taken by float charger, thus keeping the battery sections in floating condition. In case of failure of float charge the D.C. load is taken care of by the batteries. Secondly, at the time of heavy D.C. drawal the output voltage of the trickle charger falls down and the battery supplies the excess load causing the better voltage to fall down rapidly. In such a case the charger has to be switched on immediately.
It charges the batteries as well as feeds the connected load. To operate the boost charger trickle charger has to be made “OFF” (D.C. output switch M.C.C.B-I of the trickle charger is to be made off).
CHECKING OF BATTERY:
Normally while the batteries are in the charged condition the specific gravity of the electrolyte should be kept at 1200 ± 0.005 at 27 0C. This should be checked once a shift at least 24 hrs intervals. This can be ascertained by taking the specific gravity of the pilot cells only. The specific gravity of the electrolyte is important because it indicates the state of charge of batteries while it is in operation.
The level of the electrolyte should be checked while checking the batteries
NOTE: When the boost charger is made “ON” the following points are to be kept in mind.
- When the cell voltage reaches 2.4V the charging current to be reduced to 42 amp approx.
- During this time hourly specific gravity voltage & temperature of the cells should be measured.
When the specific gravity of electrolyte reaches 1.200, voltage per cell reaches 2.7V approx. at a temperature of the electrolyte below 480C, the charge is completed. During charging if the temperature rises beyond 48 0C, the charging current should be reduced so that it will not exceed 48 0C. After observing the specific gravity of 1.200 & Volt per Cell 2.7 V for three consecutive readings at an interval of one hour, the boost charger to be made Off & the batteries should be charged by float charger and kept in auto.
CHANGING OVERLOAD FROM D.C.D.B – I TO D.C.D.B – II OR VICE – VERSA.
In case of maintenance or fault in Battery set-I, the load can be transferred to battery set-II and vice versa. In such case Bus-coupler is to be made on DCDB Incommer – I to be made ‘OFF’. AC supply to Charger – I to be made ‘OFF’.
D.C. EMERGENCY SUPPLY ON:
In the case of D.C., emergency supply from external source channel 5 will glow them hooter will also come.