In some fatal cases like insulation breakdown in VCB insulator posts, short circuits of tripping/closing coils, etc. in the sub-station, the rectification usually requires hours or even days depending upon the availability. Power interruption for lengthy periods is not a very desirable situation whatever the condition inside the substation. In such cases, the operators must be intuitive enough to think out of the box to resume power supply via a temporary solution i.e. Diesel Generator.
Main Parts Of A Diesel Generator
- Diesel Engine: The diesel engine is the primary component of the generator and is responsible for converting the chemical energy in diesel fuel into mechanical energy by combustion. It consists of cylinders, pistons, a crankshaft, and other components that work together to generate rotational motion.
- Fuel System: The fuel system supplies diesel fuel to the engine for combustion. It includes a fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filters, and fuel injectors. The fuel tank stores the diesel fuel, the fuel pump delivers fuel from the tank to the engine, and the fuel filters remove impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. The fuel injectors atomize the fuel and inject it into the combustion chamber of the engine for combustion.
- Exhaust System: The exhaust system is responsible for removing the combustion gases from the engine after combustion. It includes an exhaust manifold, muffler, and exhaust pipe. The exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from the engine cylinders, the muffler reduces the noise generated by the engine, and the exhaust pipe directs the gases away from the generator.
- Cooling System: The cooling system is responsible for regulating the temperature of the engine and preventing it from overheating. It includes a radiator, cooling fans, coolant pump, and thermostat. The radiator dissipates heat from the engine, the cooling fans circulate air over the radiator to cool the coolant, the coolant pump circulates the coolant through the engine, and the thermostat regulates the flow of coolant to maintain the desired temperature.
- Alternator: The alternator, also known as the generator head, is responsible for converting the mechanical energy generated by the engine into electrical energy. It consists of a rotor and stator that work together to produce electricity through electromagnetic induction. The electrical power generated by the alternator is used to power electrical loads or stored in batteries for later use.
- Control Panel: The control panel is the interface that allows the operator to control and monitor the operation of the diesel generator. It typically includes switches, gauges, and indicators for controlling the engine speed, monitoring the electrical output, and monitoring various parameters such as fuel level, oil pressure, and temperature. It may also include safety features such as circuit breakers and alarms to protect the generator and connected loads.
- Starting System: The starting system is responsible for starting the diesel engine. It typically includes a starter motor, battery, and associated wiring. The starter motor cranks the engine to initiate combustion, and the battery provides the electrical power to operate the starter motor.


Name Plate of DG Set
ADVANTAGES OF ADOPTING DIESEL POWER
■ Low installation cost
■ Short delivery periods and installation period
■ Higher efficiency (as high as 43 – 45 %)
■ More efficient plant performance under part loads
■ Minimum cooling water requirements,
■ Adopted with air cooled heat exchanger in areas where water is not available
■ Short start-up time
Disadvantages
- Environmental Impact: Diesel generators emit air pollutants during operation, including particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and greenhouse gases (GHGs). These emissions contribute to air pollution and can have negative environmental and health impacts, such as air quality degradation, respiratory health issues, and contribution to climate change.
- Noise Pollution: Diesel generators can generate significant noise levels during operation, which can be disruptive and undesirable in residential areas or other noise-sensitive environments. The noise can be a nuisance for nearby residents and may require additional measures, such as sound barriers or soundproofing, to mitigate the impact.
- Fuel Dependence: Diesel generators rely on diesel fuel, which is a fossil fuel and requires a steady supply of fuel for continuous operation. This dependency on fossil fuels can result in price fluctuations and availability issues, and it also contributes to carbon emissions and environmental concerns associated with the extraction, transportation, and combustion of fossil fuels.
- Maintenance and Operating Costs: Diesel generators require regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and other servicing, to ensure their reliable operation. The costs associated with maintenance and repairs can add up over time and increase the overall operating costs of diesel generators.
- Emissions Regulations: There are strict emissions regulations in many jurisdictions that govern the emissions from diesel generators, which may require additional equipment, controls, or upgrades to meet the regulatory requirements. Compliance with these regulations can add to the costs and complexities of operating diesel generators.
- Size and Weight: Diesel generators can be large and heavy, which may require significant space for installation and can pose logistical challenges for transportation and handling. This can limit their use in certain applications where space is constrained or weight limitations exist.
- Startup Time: Diesel generators typically require a startup time to reach their full power capacity, which may range from a few seconds to several minutes, depending on the size and type of generator. This startup time may not be suitable for applications that require instantaneous power backup, such as for sensitive electronic equipment or critical processes.
- Carbon Footprint: Diesel generators are a significant source of carbon emissions due to the combustion of diesel fuel, which contributes to climate change. As there is increasing global concern about carbon emissions and environmental sustainability, the carbon footprint of diesel generators may be considered a demerit in certain contexts.
Operational Aspects of DG Set
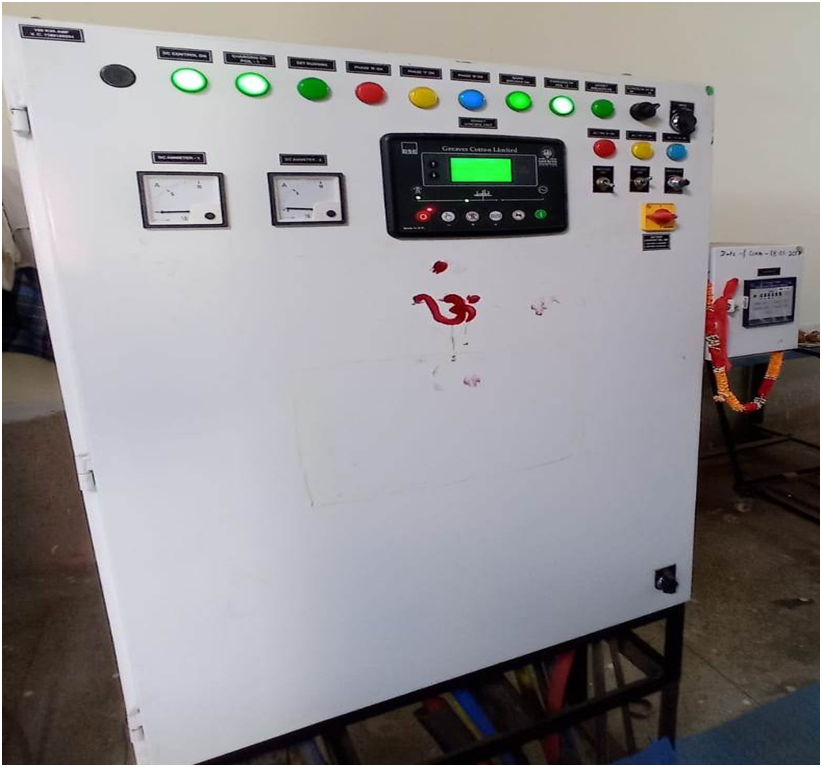

1. RED BUTTON- Used to initially stop the engine.
2. MANUAL OPERATION SELECTOR SWITCH(manual hand symbol indicated switch)- It is located closely right near the RED BUTTON switch and used to manually operate the DG SET. Press the GREEN BUTTON after switching ON the manual operation switch.
3. TOWER SYMBOL INDICATING SWITH- Usually selecting for disconnecting the Station load from Station supply to DG SET supply.
4. AUTO MODE SWITCH- Press it for automatic operation of the DG set.
5. HOOTER – Usually used for reset alarm.
6. GREEN BUTTON- For initially start the DG SET engine in manual operation mode.
7. SPEED POT –Unfortunately If the RPM of the engine is reduced below 1500 then the frequency is also reduced so to overcome this problem make it rapidly “ON & OFF” to maintain the required speed hence the frequency
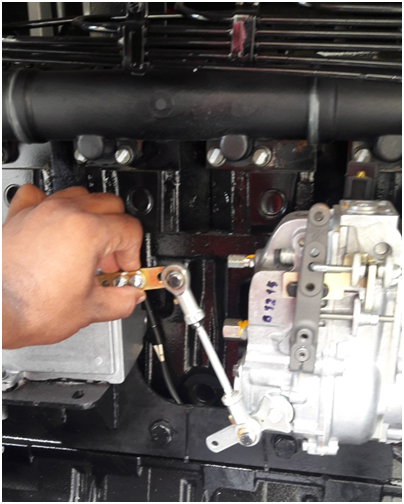
Maintenance of DG Set
During the winter season engine is jammed due to semi-solid engine oil(density increases) as in automobiles. So to heat the engine, manually operate the lever. (Up and down as shown in figure)

Maintenance Aspects
- Battery Set
- Check the battery electrolyte level. …
- Cleaning and tightening the battery terminals. …
- Check the terminal voltage. …
- Start the generator frequently
- Coolant level should be monitored
- Lubrication has to be done periodically.
Energy Saving Measures for DG Sets
- Ensure steady load conditions on the DG set, and provide cold, dust-free air at the intake
- Improve air filtration.
- Consider fuel oil additives in case they benefit fuel oil properties for DG set usage.
- Calibrate fuel injection pumps frequently.
- Ensure steady load conditions, avoiding fluctuations, imbalance in phases, and harmonic loads.
- Carry out regular field trials to monitor DG set performance, and maintenance planning as per requirements

