INTRODUCTION
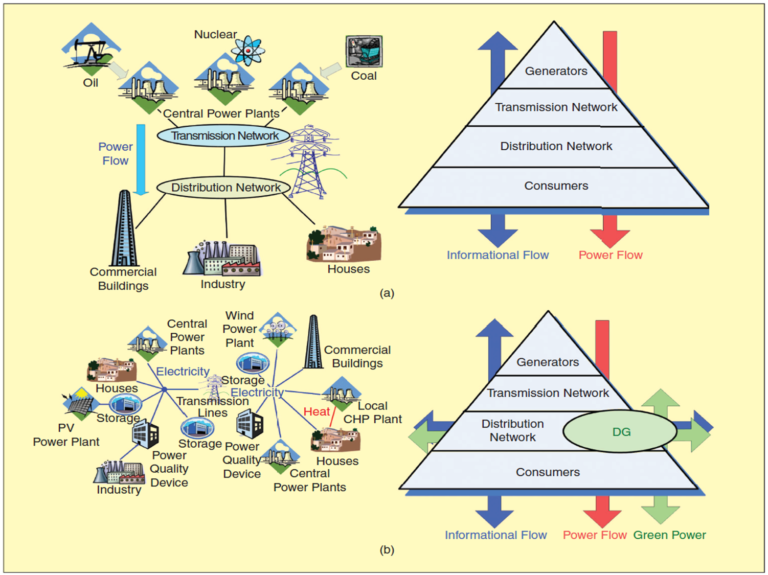
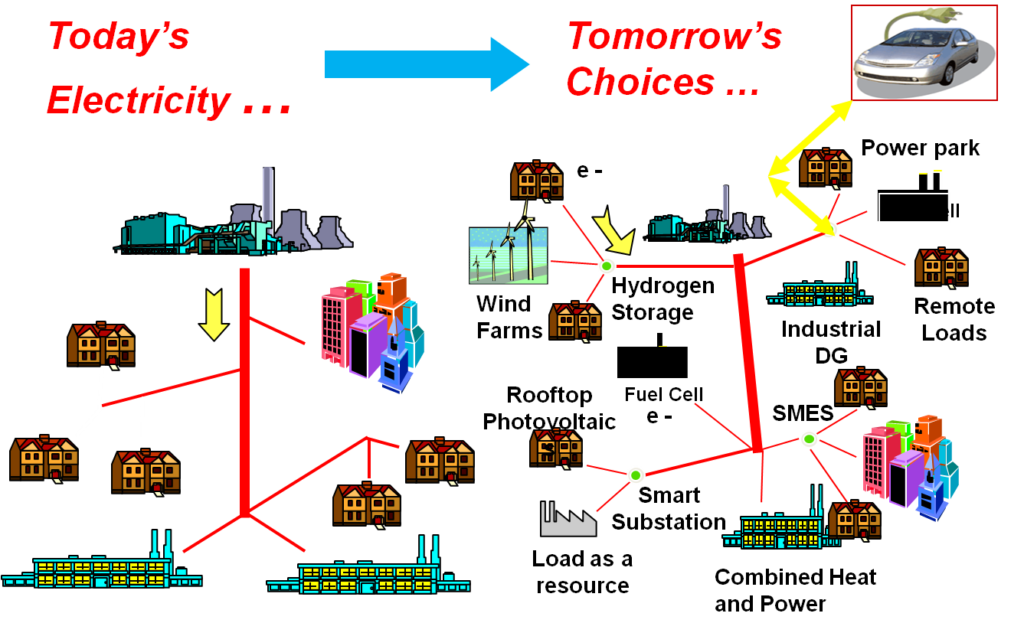
The increase of energy demand is pushing research interest in several distinct directions. Among these, distributed power plant is one of the most promising both technologically and from an economic viewpoint. In fact, decentralized generators (DG) can be located anywhere, even close to the consumer, thereby greatly reducing costs and distribution losses as well as significantly increasing overall reliability.
Moreover, choosing suitable generators, and cogeneration capability, i.e. the concurrent production of both heat and electricity can be achieved, boosting the total energy efficiency by up to 80%, or allowing regeneration. In addition to these advantages, DGs can provide either primary (during normal operations) or backup power (during grid outages), thus eliminating the need for an additional uninterruptible power supply (UPS).
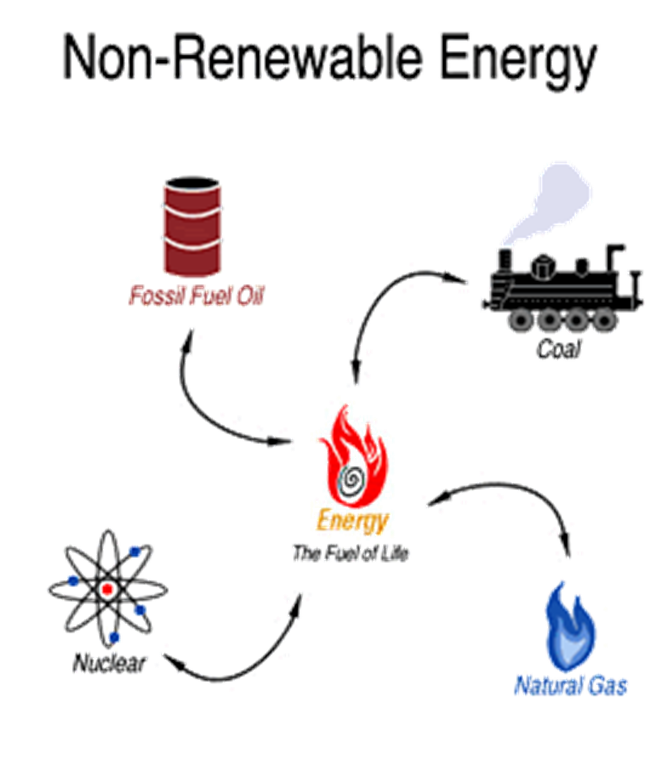
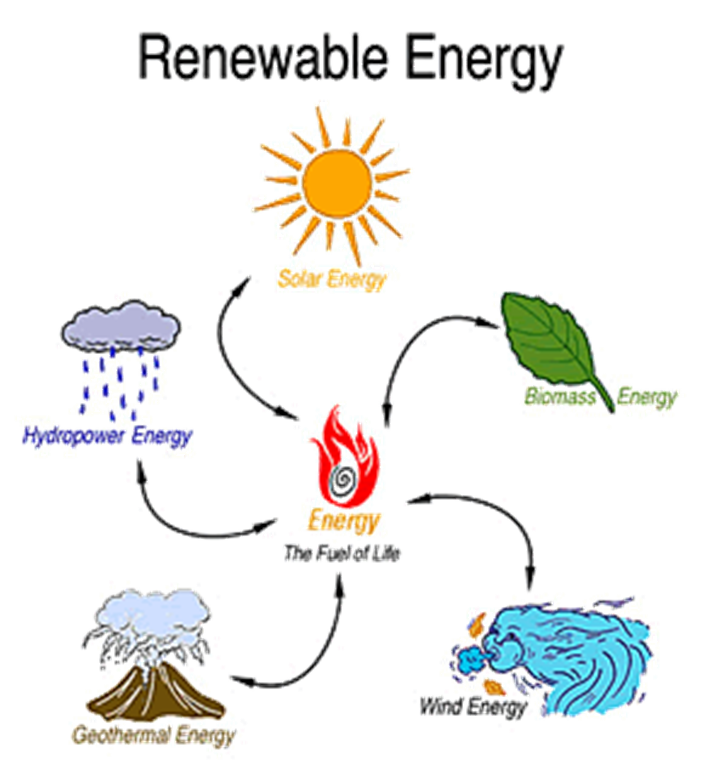
Renewable Generation:
- Solar Photovoltaics (PV)
- Wind Turbines
- Small Hydro
- Biomass and Biogas
Energy Storage:
- Batteries (e.g., lithium-ion, flow batteries)
- Thermal Storage (e.g., ice storage, molten salt)
IMPORTANCE OF POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTER IN DISTRIBUTED GENERATION
DG systems are highly intermittent power generation systems, and their power output depends heavily on natural conditions. To connect DG systems with the utility grid, various grid code requirements must be satisfied. But as DG systems are fragile and highly intermittent, a power electronics converter plays a vital role.
Whenever a DG system is required to be connected to the utility grid, two types of converters come into the picture. First is the Source-side converter, which helps ensure maximum power point tracking (MPPT); the other is the Grid-side converter, which helps maintain the grid connection standards. The proper operation of the grid-connected inverter system is determined by grid voltage conditions such as phase, amplitude, and frequency. In such applications, accurate and fast detection of the phase angle, amplitude, and frequency of the grid voltage is essential.
Role in Smart Grids and Decentralized Energy Systems
DERs are central to the development of smart grids, which use digital communication technology to manage electricity more efficiently. DERs also contribute to:
- Microgrids: Localized grids that can operate independently.
- Virtual Power Plants (VPPs): Aggregated DERs coordinated to act like a single power plant.
- Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading: Consumers can buy/sell energy among themselves.
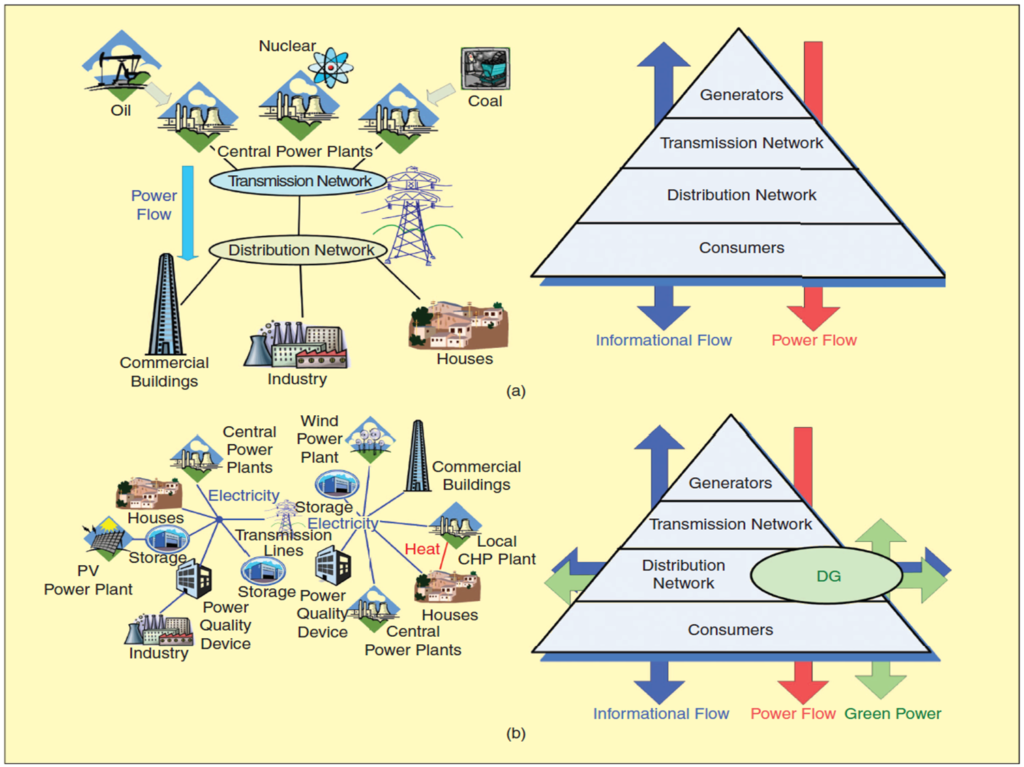
Reasons for installing DG include:
_ Combined heat and power plants (high efficiency)
_ Standby/emergency generation (enhanced reliability)
_ Using DG as a cost-effective source of peak power
_ Reduction in grid losses (typically saving 10–15%)
_ Provide voltage support and power factor correction
_ Grid investment deferment
_ Green power, renewables are well placed as DG plants
_ Premium power, high-quality supply for 24/7 services.
Challenges
- Grid Integration: Variable output from renewables can strain grid management.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Outdated policies may not support DER deployment.
- Interoperability: Ensuring DERs from different vendors work together seamlessly.
- Cybersecurity: Increased entry points can pose security risks to the grid.
Policy and Market Trends
- Incentives for rooftop solar and battery storage.
- Net metering and feed-in tariffs.
- Increasing focus on carbon neutrality and energy decentralization.