This electrical Insulator training course introduces basic safe operational and field diagnostics of insulators with a focus on safe operation, testing, and maintenance of the insulators normally installed in substations.
What is an insulator and its types?
The insulator is a device intended for electrical insulation and mechanical fixing of equipment or conductors which are subject to electric potential differences.
Based on Material
Porcelain
Porcelain insulators are widely used in overhead power transmission and distribution systems. They are made of ceramic materials, such as porcelain, which have high mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation properties. Porcelain insulators can withstand high voltages and are resistant to weather and environmental conditions.
Glass
Glass insulators were commonly used in early electrical systems but are now primarily used for decorative purposes or in low-voltage applications. Glass insulators have good insulating properties but are more fragile compared to porcelain insulators.
Polymer
•-Polymer insulators are similar to composite insulators but are made entirely of polymer materials. They provide good electrical insulation, excellent resistance to environmental conditions, and are lightweight. Polymer insulators are commonly used in distribution systems and indoor electrical applications.
PVC
Insulating tapes and coatings are used to provide insulation and protection for electrical conductors or components. They are typically made of materials like rubber, PVC, or silicone and can be applied as a layer or wrapped around the conductors.
Based on Application
1. Transmission line insulators
a. Disc insulators
b. Long rod insulators
c. Line post insulators
2. Substation insulators
a. Solidcore insulators
b. Hollow insulators
3. Traction insulators
Stay arm, Bracket, 9 ton, operating rod etc.
4. Distribution insulators
Pin, shackle, guy strain etc.

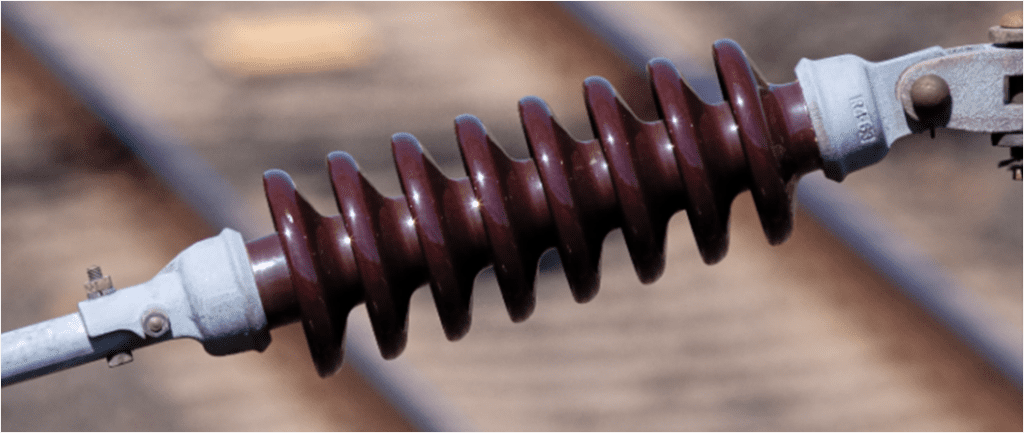
Long rod insulators
•Long rod insulators are used in high voltage transmission lines —voltages ranging from 33kV to 1200kV and Studies reveal that porcelain long rod insulators have superior electrical and mechanical properties, power arc and interference voltage behavior compared to the traditional cap & pin type disc insulators
•Porcelain long rod insulators are of solid core type “A” construction and are puncture-proof. These insulators are designed to provide flexible support while at the same time ensuring that the tensile load requirements in service are met. The insulators are made of high-quality Aluminous porcelain meeting the requirements of C130 in accordance with the IEC: 60672.
• The long rod insulators are subjected to static and dynamic loads including wind load, ice load, conductor galloping, short circuit forces, etc., and are designed to withstand such loads constantly and continuously for decades.
These are some of the commonly used types of electrical insulators. Each type has its own advantages, limitations, and specific applications where they are most suitable. The selection of an appropriate insulator depends on the specific requirements of the electrical system or equipment.
DEFECTS OBSERVED IN INSULATORS
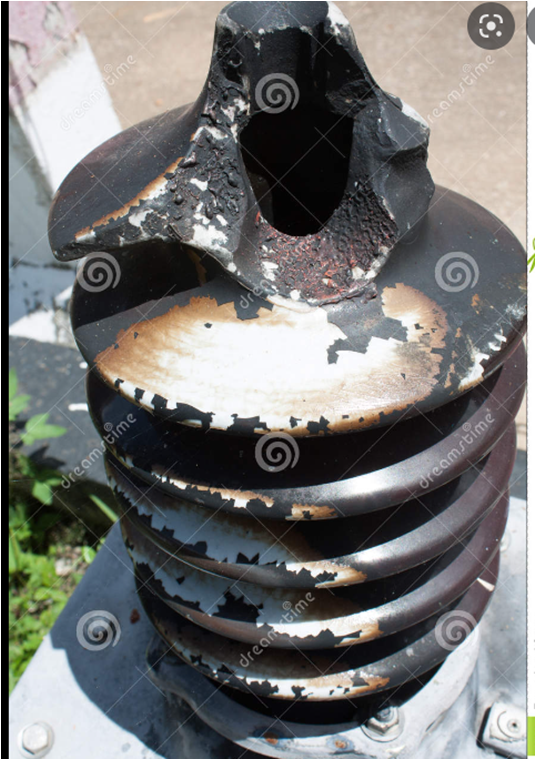

Cracking of Insulator
Defective Insulation Material
Porosity in The Insulation Materials
Improper Glazing on Insulator Surface
Flash Over Across Insulator
Mechanical Stresses on Insulator
Maintenance
Maintenance of insulators in a substation is important to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. Regular maintenance practices help prevent issues such as flashovers, contamination, and degradation of insulating properties. Here are some common maintenance activities for insulators in a substation:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect insulators visually for any signs of physical damage, cracks, chips, or discoloration. Check for any loose or broken hardware, such as pins, caps, or fittings. Inspect the overall condition of the insulators and ensure they are properly aligned and mounted.
- Cleaning: Insulators can accumulate dirt, dust, pollution, and other contaminants over time. Regular cleaning is essential to maintain their insulating properties. Use appropriate cleaning methods, such as water washing, with mild detergents or specialized insulator cleaning solutions. Avoid using abrasive materials or excessive water pressure that may damage the insulator surface.
- Contamination Control: Substations located in areas with high pollution levels or industrial environments may experience insulator contamination due to deposits of dust, industrial emissions, or bird droppings. Insulators should be regularly inspected and cleaned to remove such contamination, as it can lead to reduced insulation performance and increased risk of flashovers. In some cases, applying specialized hydrophobic coatings or pollution-resistant coatings can help prevent contamination buildup.
- Leakage Current Measurement: Periodic measurement of leakage current can provide insights into the condition of insulators. Excessive leakage current may indicate surface contamination, degradation, or the presence of conductive paths. Conduct regular leakage current measurements using appropriate equipment and compare the results against acceptable limits defined by standards or manufacturer guidelines.
- Inspection of Hardware: Check the condition of the hardware associated with insulators, including clamps, fittings, pins, and connectors. Ensure that all hardware is securely fastened and tightened. Replace any damaged or corroded hardware to maintain the integrity of the insulator system.
- Thermal Imaging: Utilize thermal imaging cameras to identify any abnormal temperature patterns on insulators. Hotspots may indicate localized heating due to electrical discharge or excessive current flow. Detecting such hotspots early can help prevent insulation failure and equipment damage.
- Periodic Dielectric Testing: Periodic dielectric testing involves subjecting insulators to high-voltage tests to evaluate their insulation strength. This helps identify any potential weaknesses or degradation of insulating properties. Dielectric testing is typically performed using specialized testing equipment and should be carried out according to recommended schedules and procedures.
- Record Keeping: Maintain comprehensive records of inspection, cleaning, testing, and maintenance activities performed on each insulator. This documentation can help track the condition of insulators over time, identify recurring issues, and schedule future maintenance activities.
It is crucial to follow proper safety procedures and guidelines while performing maintenance tasks on insulators within a substation. Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations and industry best practices for specific maintenance requirements related to the insulators used in your substation.