INTRODUCTION
High-voltage transmission systems are vital for delivering electricity across vast distances. However, they are vulnerable to transient overvoltages caused by lightning strikes, switching surges, and fault-induced transients. These surges can damage equipment, cause outages, and lead to high repair costs. That’s where Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) play a key role in shielding the grid.
This article explores the types, principles, and applications of SPDs in transmission grids and lines.
🌩️ Why Surge Protection is Essential in Transmission Systems
Surges in transmission systems can originate from:
- Lightning strokes on overhead lines or nearby ground
- Switching operations in substations
- Load rejection or capacitor bank switching
- Faults or insulation failure
Unmitigated surges can:
- Damage transformers, bushings, circuit breakers, and insulators
- Trigger relay malfunctions or false tripping
- Cause insulation flashovers
| Location | Purpose | Device Used |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Lines (66 kV and above) | Protection from direct lightning strokes | Line Arresters, Shield Wires |
| Substation Busbars | Surge control from line-side disturbances | MOV Arresters |
| Transformer Terminals | Protect winding insulation and bushings | Transformer-connected Arresters |
| Circuit Breakers & GIS | Internal switching surge mitigation | Station Class Arresters |
| Line Terminations | Prevent surges from propagating | End-of-line Arresters |
Where is the surge arrester placed in the substation?
To protect a unit of equipment from transients occurring on an attached conductor, a surge arrester is connected to the conductor just before it enters the equipment.Lightning arresters are often referred to as “soldiers of the power system” because they play a crucial role in protecting electrical systems and equipment from the destructive effects of lightning strikes. Just like soldiers defend and protect their territory, lightning arresters safeguard power systems.
Lightning is a natural phenomenon that generates extremely high voltages and currents. When lightning strikes occur, they can induce surges or transient overvoltages in power lines, which can potentially damage or destroy electrical equipment connected to the system. These overvoltages can disrupt power transmission and distribution, cause equipment failure, and even pose a safety hazard.
What is an arrester used for?
The purpose of using a surge arrester is to always limit the voltage across the terminals of the equipment to be protected below its insulation to withstand voltage. This is achieved by connecting elements with an extremely nonlinear voltage-current characteristic (varistor) in parallel to the terminals of the equipment.
How Does a Lightning Arrester Work?
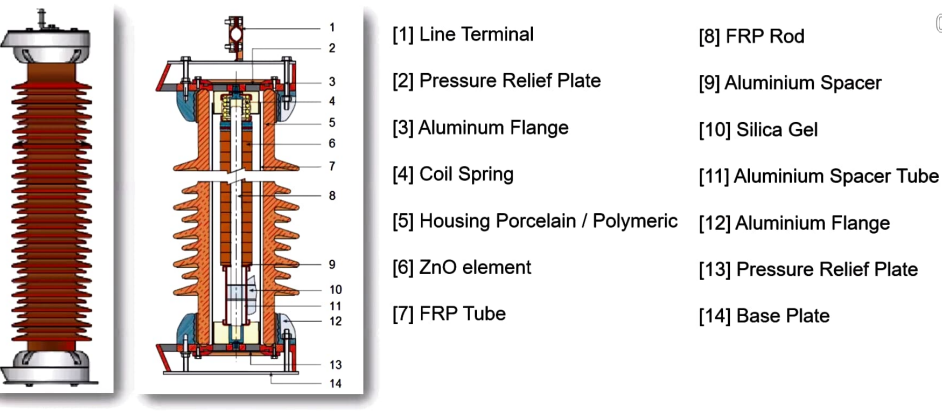
- Metal oxide (MO) surge arresters containing ceramic MO elements mainly made from zinc oxide and bismuth oxide are used.
- The resistor elements offer non-linear resistance such that for normal frequency the power system voltage resistance is high and the lightning arrester does not conduct.
- When a surge voltage travels along the line and comes to the arrester the gap breaks down and the resistance is low the surge is diverted to the earth.
- After a few microseconds, the surge vanishes and the power frequency voltage is set up across the arrester and the arc current reduces.
- All electrical equipment in an electrical system needs to be protected from voltage surges.
- The rating of the arrester, the class of the arrester, and the location of the arrester all play a part in surge protection.
- Surge arresters protect the equipment of transmission and distribution systems, worth several magnitudes more than the arresters themselves, from the effects of lightning and switching overvoltages.
What are the tests conducted on surge arresters?
- Insulation Withstand Test- is an electrical test carried out on a component or product to determine its insulation strength.
- Residual Voltage test This test confirms that no dangerous voltages are present after the supply has been removed as a result of circuits retaining a charge.
- Power Frequency Voltage versus Time Curve
- Internal Partial Discharge Test
- Moisture ingress Test (For Station type Surge Arrester)
Causes for Failure of Metal Oxide Surge Arresters
- Incorrect arrester specification corresponding to actual system voltage and overvoltage stress
- Overloading due to:
o Temporary overvoltages (cracking, puncturing)
o Switching overvoltages (cracking, puncturing, and flashover)
o Lightning overvoltage (change of characteristic/aging, flashover, puncturing).
- External pollution or moisture penetration
- The consequence of aging: Increase in the continuous resistive leakage current. This is a good indicator of the arrester’s condition.
Methods for Monitoring of Degradation of MOSA
- Visual inspection
Locating external abnormalities on the arrester gives practically no information about the internal of the arrester.
- Surge counters
Frequently installed on MOSA, but has no practical use for diagnosis of the condition of the arresters.
- Temperature measurements–Thermo Vision
Frequently used method. Detects the increased block temperature on the housing surface of the arrester.
- Leakage current measurements
For in-service testing, the method with the indirect determination of the resistive leakage current with compensation for harmonics in the voltage provides the best available information quality with respect to diagnostic efficiency.
📌 Conclusion
Effective surge protection is a critical component of transmission system reliability. From lightning-induced overvoltages to switching transients, SPDs like MOV arresters and line arresters offer robust defense mechanisms. Proper selection, placement, and monitoring ensure long-term performance and safety of high-voltage infrastructure.
📖 Related Articles on ElectricKnowHow.com
- Understanding Distribution Protection: Fuses, Relays & Reclosers
- High Voltage AC Transmission – An Overview


