In our sub-stations, there are multiple equipment that perform their function to distribute the power in a good way. In this interesting article, we are going to discuss the nameplate parameters of isolators. Let’s start!
Isolators/Dis-connectors
An isolator is used to disconnect the circuit after removing the load from it. It is different from a circuit breaker as an isolator is an off-load device and a circuit breaker is an on-load device. An isolator is a type of switch used in a substation to disconnect the circuit in case of maintenance.
There are two purposes of this switch in the sub-station:
- To isolate the particular area of the sub-station
- To re-route the power flow
In order to carry out maintenance on a circuit breaker we need to open the isolator on both sides of the circuit breaker to isolate the area completely. We cannot operate the isolator when there is supply present but we can operate the breaker in the presence of a supply. This is the short idea of how isolators work in our sub-stations.
✅ Nameplate Importance
- Used during commissioning checks
- Helps in spare part ordering
- Essential for maintenance planning
- Required during technical audits and inspections
Nameplate Detail of an Isolator/Dis-connector
Now we will discuss all the parameters that are mentioned on the nameplate of an isolator.
- First, there will be the manufacturer’s name.
- Then there will be the project, client name, contractor name, and manufacturing year. These are the project-related things.
- Next, we have rated voltage indicating that this dis-connector is designed for 420kV rated voltages (in our case). You can see below the nameplate detail:
There is something missing on the nameplate of this dis-connector. Read out the article to find that missing value.
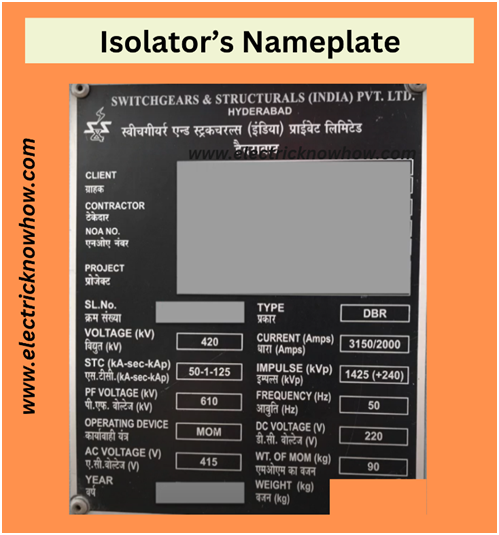
You can verify all the parameters in this image.
- Next, we have STC which represents short-time current. You can see 50-kilo ampere for 1-second meaning that this dis-connector can withstand 50-kilo ampere of short-circuit current for 1 second and it is tested for the same value. There is also one value mentioned which is 125. This value is the making current or a dynamic current. In the case of a circuit breaker, if it closes during an existing fault the short-circuit current may rise up to a certain value and it is generally as per IEC standards. It is 2.5 times of rated short circuit current.
If we multiply 2.5 with dated short current you can get the same value mentioned on the nameplate of the dis-connector.
- Next is power frequency voltages in RMS. Power frequency voltage can be generated due to these reasons:
- Phase to Earth Fault
- Load rejection
- Ferro resonance
- Ferranti effect
This dis-connector is tested for the same value and can withstand a certain value of power frequency voltage in the above faults.
The lightning impulse voltages are generally generated due to lightning strokes. 1425kV impulse voltages are applied to Earth. Meanwhile, 240kV will add up to 1425kV to provide peak value for lightning impulse voltage which is applied across the isolating distance. It means from one side they will give one shot of 1425 kV peak and from another side, they will give one shot of 240 kV peak.
- Next is the operating device mechanism so here you can see it is mentioned as MOM (indicates motor operated mechanism). The dis-connectors generally come in two different operating mechanisms one is motor operated and another is manual-operated. In the manual mechanism, you have to go near the dis-connector and manually spin the handle to open or close the disc connector.
- Next is AC voltages on which the three-phase AC motor will be operated. It is 3 phase-415V AC voltages in our case.
- Next, we have the manufacturing year of the product.
Next is the type of dis-connector so it is mentioned here as DBR which indicates double brake type dis-connector.
- Now we will discuss these types of dis-connectors.
- The first is the double break type. This type of dis-connector opens from both ends that is it breaks from both sides and that is why it is called a double break disc-connector. This type of discount is generally used between 11kV to 420 kV.
- Next is the horizontal center break. It breaks from the center and it is also called a single break because there is only one break which is also called a single break this connector is also used between 11kV to 420 kV.
- Next is Knee-type dis-connectors which are only used for 800 kV. Their opening or closing looks like when you bend your knee.
- There is also photograph type which is used for 245kV to 420kV.
- The next thing is the rated current and here you can see this particular dis-connector is designed for a rated current of 3150 amperes or 2000 amperes.
- Next is the rated frequency which indicates the rated frequency for which this dis-connector is designed.
- Moving forward there is a DC voltage now DC voltage is required alongside the control box which controls the dis-connectors.
- The last item is the weight of MOM and the weight of the total isolator.
Here the manufacturer missed two things:
One is the standard according to which the isolator is manufactured. It is IEC 62271-102 in our case (Air Insulated Dis-connector).
The second thing is switching the voltage for the 420kV operated isolator.
Conclusion:
We have discussed the main parameters of an isolator’s nameplate in detail. These include project-related things, rated current, DC voltage to control the dis-connector, the lightning impulse, and power frequency voltages. There is a standard according to which an isolator is manufactured.
You can comment down your feedback!

