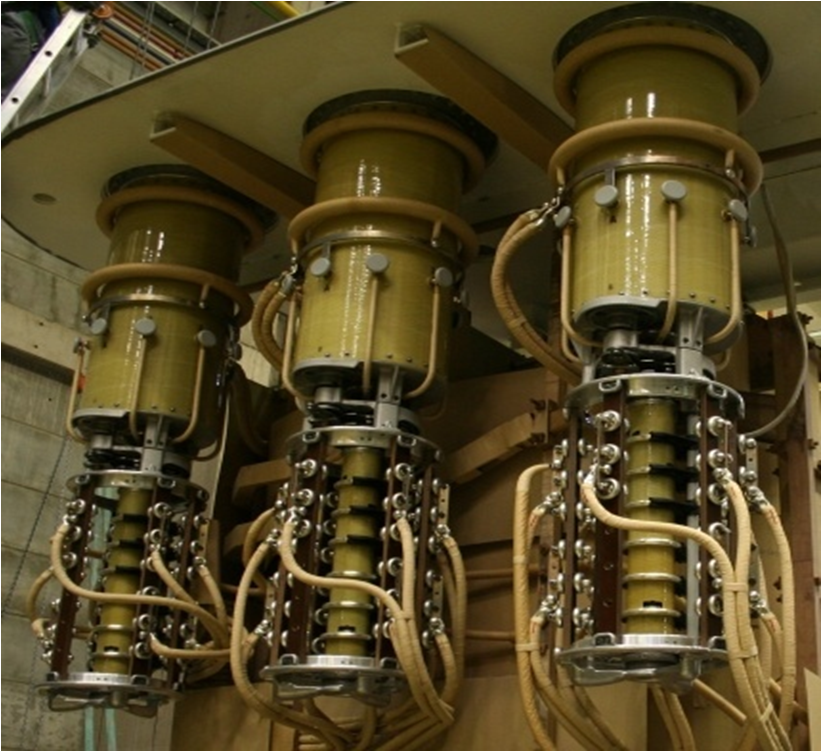
Introduction
After electricity generation in turbines or other generation methods, transformers play an important role in the transmission and distribution of electrical power. They maintain the voltage level by step-up and step-down voltages. They are responsible to transmit electric power from one main circuit to another circuit. To maintain these voltages in the transformer we use the concept of Tap Changing.
Tap Changing:
The main purpose of the Tap changer is to regulate the transformer output voltage by changing the turn ratio of the transformer in the winding. Tap Changer is a mechanism to complete this step. So, such transformers that have the option to change output voltage are called tap-changing transformers
Why we need tap changing?
We know that we connect the load at the secondary side of the transformer means at the output side of our transformer. When we increase the load it leads to a decrease in the magnitude of output voltage. For example in our sub-station, we have a transformer with a voltage rating 132/33kV. At the 33kV side, we connect our load and when the secondary side load is increased then the 33kV voltage is decreased to 32.8 or 32.6kV. Now in this condition, we need our 33kV voltages back as we want our 132/33kV voltage ratio constant.Similarly, during light load conditions, the secondary side voltage may go beyond 34KV.
We have to maintain the secondary voltage value at 33kV (in case of a decrease or increase)due to a change in load. So, in this condition to regulate the output voltage we need tap changing.
Location of Tap Changer in Transformer
Tap changer is always connected to the high-voltage side of the transformer. In our recent example of 132/33kV, tap changer will be placed at the higher voltage side mean at 132kV. You can have a look on the following picture:
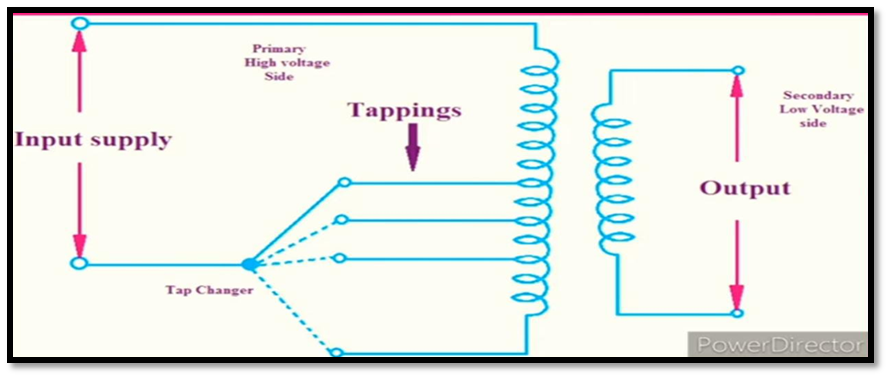
In this picture there are a number of turns are present and you can select the tap number. In the tap changer transformer number of tap changing is provided.
We know at the high voltage side of the transformer current magnitude is less, and similarly, at low voltage side of the transformer, the current magnitude is high. This is the reason we install our tap changer at high voltage side because of:
- less current magnitude and for safety purposes, to interrupt low current is easy to we use higher voltages and lower current side for tap changing as compared to high current
- Second reason is that, the transformer winding high voltage is wounded outside and low voltage side is wounded inside. So, high voltage side stays on the upper portion and low voltages side stays on the lower portion. And it is more is safer and easy to take tap out for upper side of transformer.
Working
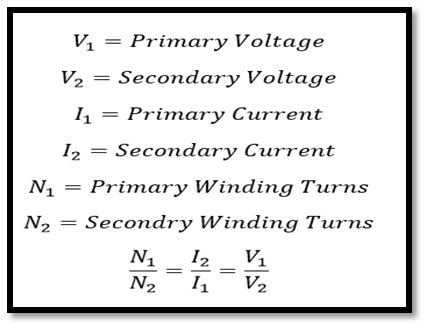
So, main work of tap changer is select these taps and change the number of turns. And when in our transformer numbers of turns are changed, that will result in voltage change. According to transformation ratio, number of turns are directly proportional to voltages.
Types of Tap Changers:
We have two types of tap changing:
- Off load tap changer
- On load tap changer
Off load tap changer
In this tap changing, we have to disconnect the transformer first from the supply. We have to isolate of supply in the transformer. So, it is called an offload transformer. Normally, distribution transformers are off-load tap changer transformers of 2.5MVA.
It is important to note that practically, we cannot change transformer tap in running condition.
On load tap changer
It is opposite to off load transformers and we can change tap in its running condition to regulate output voltages. In big transformers like in generating unit and in the transmission unit, we cannot hand trip such transformers to change the tap position. Transformers of more than 12MVA are used in our sub-stations and we cannot shut down such transformers as it will disturb the continuous electricity supply. So, we prefer load tap changing in large power rating transformers.
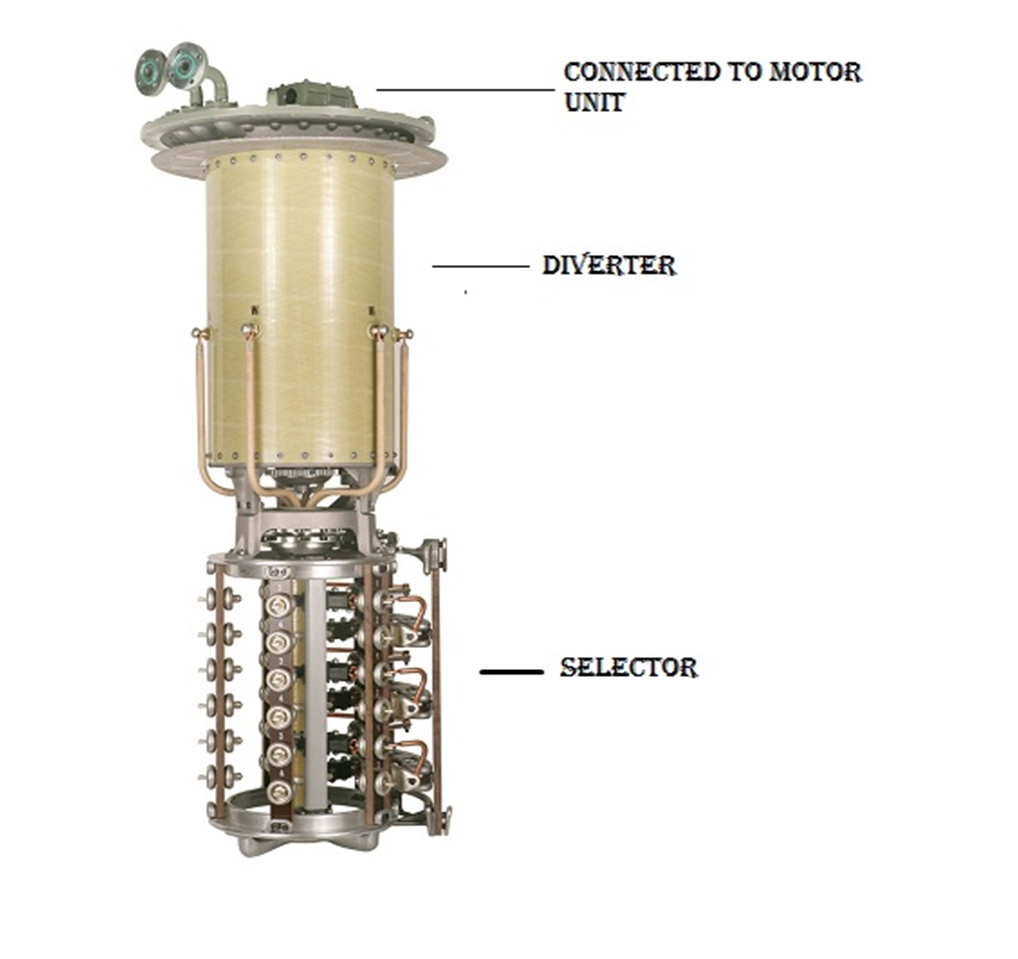
SELECTION OF LOAD TAP CHANGER:
•MVA rating
•Connection of tap winding(star or delta)
•Rated voltage and regulating range
•Number of service tap position
•Breaking capacity
•Overload capability
•Short circuit current
•Contact life


