1.INTRODUCTION
Protection of generators is a challenging task because of their system is connected to the power grid, prime mover, and DC excitation.
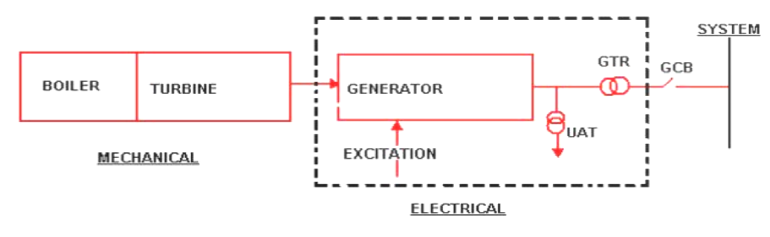
Unlike other apparatus only isolating the circuit breaker is not enough to prevent further damage as the generator would still supply power to its stator windings until the excitation is suppressed. So for isolation, it is needed to open the field to avoid any excitation and to stop the fuel supply to the prime mover.
The collective function of all forms of protection applied to large generators is, therefore, to reduce the
clearance time of all fault conditions associated with it. It is of prime importance that the protective devices
should disconnect the machines automatically if the fault is internal or if the external conditions are so
abnormal that the continued operation would result in damage.
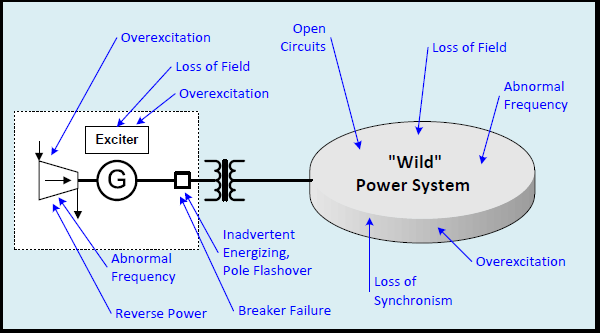
There are a number and variety of failures to which a generator may be subjected. Several protective systems
are employed, both of discriminative and non-discriminative types. Great care must be exercised in coordinating the systems used and the settings adopted.
2.GENERATOR PROTECTION SCHEMES
| Fault / Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Stator Winding Faults | Line-to-ground or phase-to-phase faults in the stator windings |
| Rotor Faults | Ground faults or field winding short circuits |
| Overvoltage / Undervoltage | Deviations from rated voltage can damage insulation or equipment |
| Overcurrent | Caused by short circuits or excessive load |
| Overfrequency / Underfrequency | Due to imbalance between generation and load |
| Overload / Overheating | Leads to insulation degradation and potential failure |
| Loss of Excitation | Causes loss of synchronism, possibly leading to system instability |
| Unbalanced Load (Negative Sequence Current) | Produces heating in the rotor due to unequal phase currents |
| Out-of-Step / Pole Slipping | Loss of synchronism with the grid |
| Reverse Power Flow | Occurs when power flows back into the generator (e.g., prime mover failure) |
| Loss of Prime Mover | Generator starts motoring and draws power from the grid |
⚙️ 3. Typical Generator Protection Schemes
| Protection Type | Device / Relay Function | ANSI Code |
|---|---|---|
| Stator Ground Fault | Ground fault relay | 64G |
| Differential Protection | Compares input/output current to detect internal faults | 87G |
| Overcurrent Protection | Trips during excessive load or short circuits | 50/51 |
| Over/Under Voltage | Protects against abnormal voltage | 59 / 27 |
| Over/Under Frequency | Detects abnormal frequency conditions | 81O / 81U |
| Negative Sequence Protection | Detects unbalanced loading conditions | 46 |
| Loss of Excitation | Measures impedance changes | 40 |
| Reverse Power Protection | Detects reverse power flow | 32 |
| Out-of-Step / Pole Slip | Detects instability due to synchronism loss | 78 |
| Overtemperature | Monitors generator winding or bearing temps | 49 |
🔄 4. Coordination and Integration
- Protection must coordinate with other system elements (e.g., transformer, bus, line protections).
- Typically managed through a Generator Protection Relay Panel.
- Integrated into SCADA or DCS systems for real-time monitoring and remote control.
🧰 5. Testing and Maintenance
- Periodic testing of:
- Relay settings and logic
- Current and voltage transformers
- Breakers and trip circuits
- Online monitoring for temperature, vibration, and insulation condition
- Use of generator protection test kits (e.g., Omicron, Doble) for accurate diagnostics
📘 Standards and Guidelines
- IEEE C37.102 – Guide for AC Generator Protection
- IEC 60034-1 – Rotating electrical machines
- NERC Reliability Standards – For generator performance and protection compliance


2 Comments
Pingback: Power System Protection – Learn With Electric Know How
Pingback: Basics of Power System Protection - Learn With Electric Know How