Here’s an overview of Power Sector Reform in Odisha from 1990 to 2025, covering key milestones, institutional changes, and outcomes:
1. Pre-Reform Era (Before 1990)
- The electricity sector was managed entirely by the State Electricity Board (SEB), specifically the Orissa State Electricity Board (OSEB).
- Characterized by:
- Poor financial health
- High transmission & distribution (T&D) losses (~50%)
- Inefficient tariff structures
- Cross-subsidization of agriculture and domestic sectors
2. Pioneering Reforms Begin (1993–1999)
Odisha was the first Indian state to launch power sector reforms under World Bank assistance.
Key Milestones:
- 1995: Orissa Electricity Reform Act passed – provided a legal framework.
- 1996: Formation of Orissa Electricity Regulatory Commission (OERC).
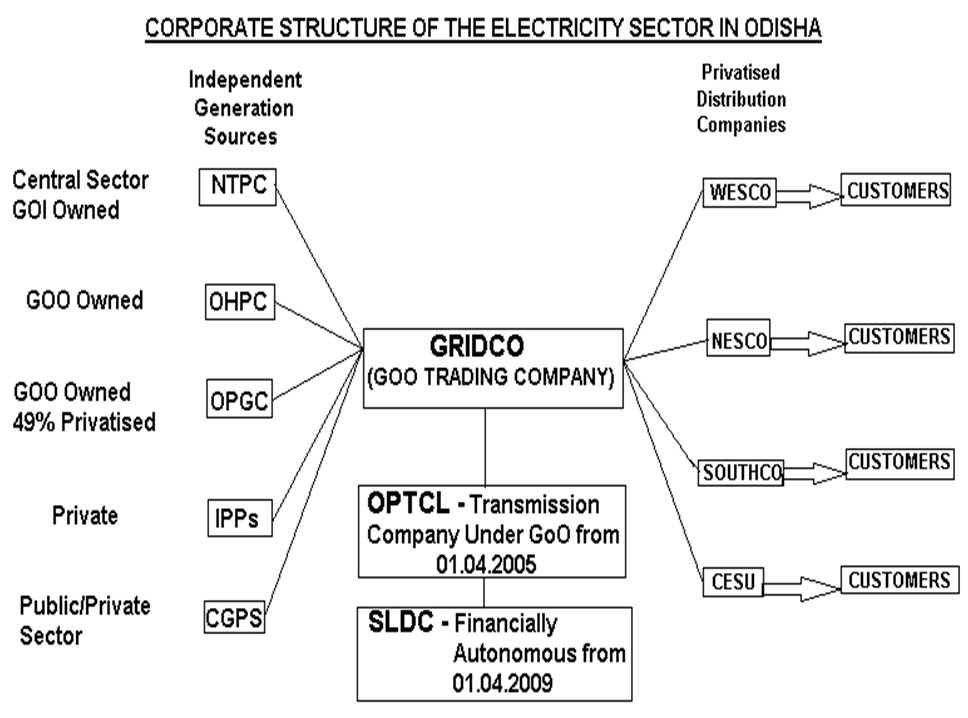
- 1996: Creation of Grid Corporation of Odisha (GRIDCO) – for transmission and bulk supply.
- 1997: Formation of OHPC (Orissa Hydro Power Corporation) and OPTCL (Orissa Power Transmission Corporation Ltd).
Orissa Electricity Regulatory Commission (OERC)–
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Establishment | Orissa Electricity Regulatory Commission (OERC) was established in August 1996 under the Odisha Power Sector Reforms Project. |
| Significance | First independent electricity regulatory body in India. |
| Delegated Authority | Took over several responsibilities and powers previously held by the State Government. |
| Key Functions | – Regulate generation, transmission, distribution, and supply of electricity in Odisha. – Promote efficiency, economy, and safety in electricity usage. – Encourage competition and private sector participation while protecting consumer interests. |
| Role in Sector Regulation | – Monitors performance of private utilities. – Ensures reasonable returns for utilities. – Acts as custodian of public interest. |
| Objective | Balance interests of stakeholders and foster a competitive, efficient, and economically sound power sector in the state. |
Unbundling of OSEB:
- Generation: Separated as OHPC.
- Transmission & Distribution: GRIDCO handled both initially.
Privatization of Distribution:
- 1999: Four distribution zones were privatized:
- CESCO (Central Electricity Supply Company)
- NESCO (North Eastern)
- WESCO (Western)
- SOUTHCO (Southern)
Ownership was given to BSES Ltd and AES Corporation (USA).
FUNCTIONS OF SLDC
The SLDC (State Load Despatch Center) is the Apex body to ensure integrated operation of the Power System in the State of Odisha. It monitors integrated grid operation for quality, security & reliability of power supply in the state of Odisha in co-ordination with ERLDC (Eastern Region Load Despatch Center).The functions of SLDC derived in accordance to the provisions U/S 32 of The Electricity Act, 2003 and Clause 2.6 of Indian Electricity Grid Code (IEGC), are:
- It exercises supervision and control over the intra-state transmission system. It keeps accounts of the quantity of electricity transmitted through the state grids.
- It is responsible for carrying out real time operations for grid control and despatch of electricity within the state of Odisha through secure and economic operation of the state grid in accordance with the grid standards and state grid code.
- It is responsible for optimum scheduling and despatch of electricity within the state of Odisha in accordance with the contracts entered into with the licensees or the generating companies operating in the state of Odisha.
- It coordinates drawal schedule from state sector generators, CPPs and for bilateral trading. It provides avenues for intra and regional exchanges.
- It telemeters real-time data from major generating plants and substations in the state.
- It issues clearance for the outage of elements for maintenance work, including state sector generators.
- It supports performing simulation and operational studies for real-time operation.
- It ensures compliance of all directions issued by RLDC to STU/generating companies/any other licensee of the state.
3. Post-Privatization Challenges (2000–2010)
- Private DISCOMs failed to reduce losses or improve efficiency significantly.
- AES exited CESCO in 2001 due to mounting losses.
- GRIDCO re-acquired management of failing DISCOMs, leading to partial reversal of privatization.
Notable Developments:
- 2005: Creation of OPTCL by separating transmission from GRIDCO.
- Introduction of Accelerated Power Development & Reforms Program (APDRP).
- Tariff revisions under OERC to ensure cost recovery.
4. Renewed Reforms & Central Schemes (2011–2020)
Key Programs:
- R-APDRP (Restructured) → IPDS (Integrated Power Development Scheme) for urban areas.
- DDUGJY (Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana) for rural electrification.
- SAUBHAGYA Scheme: Odisha achieved near 100% household electrification.
Performance Improvements:
- Gradual reduction in Aggregate Technical and Commercial (AT&C) losses.
- Use of smart meters, feeder metEnergy Meter Apex 100ering, and energy audits.
- Distribution franchising was explored in some circles.
Ownership Shift:
- 2015–2019: Odisha DISCOMs were struggling financially; performance-based incentives tied to central schemes.
5. Tata Power Takeover (2020–2021)
In a major turnaround step, Odisha handed over DISCOM operations to Tata Power via PPP (Public-Private Partnership).
Timeline:
- 2020:
- Tata Power took control of CESU (renamed TPCODL).
- 2021:
- Tata Power took over remaining DISCOMs:
- TPWODL (WESCO)
- TPNODL (NESCO)
- TPSODL (SOUTHCO)
- Tata Power took over remaining DISCOMs:
Objectives:
- Improve billing & collection efficiency
- Smart meter rollout
- Reduce losses to below 15%
- Upgrade consumer services and infrastructure
6. Recent Developments (2021–2025)
- Rapid expansion of renewable energy, especially solar:
- Solar parks and rooftop solar programs across Odisha.
- Green Energy Corridor integration for RE evacuation.
- Smart Grid Pilots initiated in urban clusters.
- Greater focus on:
- Energy Efficiency (with BEE)
- Decentralized Solar Energy
- 24×7 Power for All goals
Digitalization & IT Upgrades:
- SCADA, GIS-based asset mapping, and IT-OT convergence across DISCOMs.
- Customer mobile apps, grievance portals, and prepaid metering.
7. Summary of Outcomes (1990–2025)
| Area | Before Reform | 2025 (Current Status) |
|---|---|---|
| Utility Structure | Vertically integrated OSEB | Unbundled with PPP DISCOMs |
| AT&C Losses | ~50% | Target <15% (varies by zone) |
| Tariff System | Politically driven | Cost-reflective with OERC regulation |
| Electrification | Limited, rural backlog | 100% village & ~100% HH electrification |
| Consumer Services | Manual billing, poor grievance redressal | IT-enabled, mobile apps, 24×7 helplines |
| Private Sector Role | None | Tata Power manages all 4 DISCOMs |
Conclusion
Odisha set the benchmark for early power sector reforms in India. Despite initial setbacks post-privatization, the state’s decision to involve Tata Power in managing all DISCOMs revived reform momentum. With digital transformation, renewable energy focus, and strong regulatory mechanisms, Odisha is emerging as a model for PPP-led power distribution reform in India.


