Introduction
Grid substations operating at 220kV, 132kV, and 33kV voltage levels form the backbone of transmission and sub-transmission networks. Protecting these substations ensures system reliability, personnel safety, and equipment longevity. Faults, if not isolated promptly, can escalate into widespread outages. This article explores the essential protection schemes, key components, and best practices for such substations.
Introduction to power system protection and switchgear
Understand operations & characteristics of various electromagnetic and static relays
Understand the operations of various types of circuit breakers and their ratings
Contribute to the system reliability improvement
Key Components of Substation Protection Systems
Instrument Transformers (CTs and PTs): Measure high voltage/current for protective relays.


Protection Relays: Monitor abnormal conditions and initiate breaker operations.
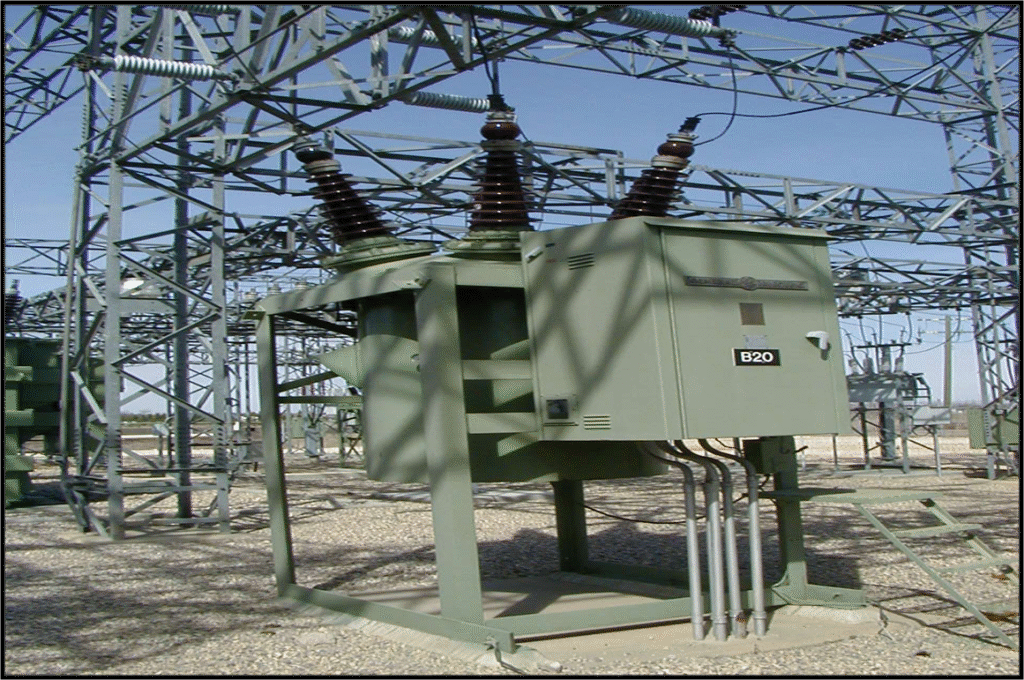
Circuit Breakers: Interrupt fault currents upon tripping signals.
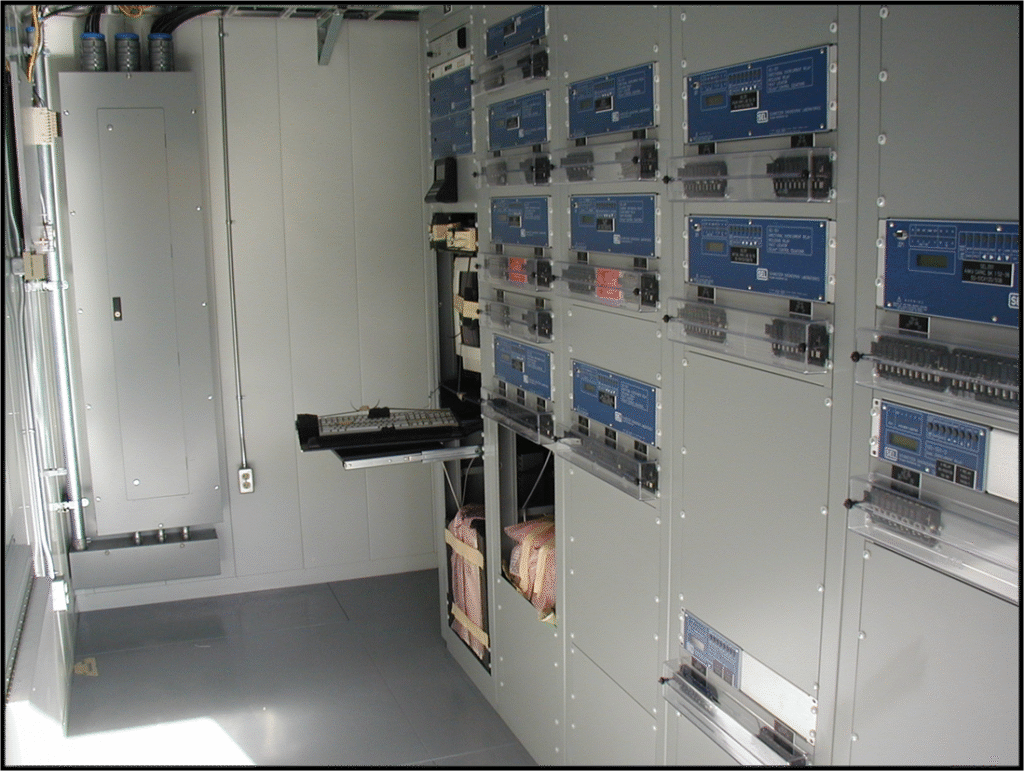
Trip Circuits and Batteries: Ensure reliable operation of protection schemes.
Communication Systems: Enable coordination between remote terminals via PLCC, fiber, or IEC 61850.
Best Practices:
Redundancy: Avoid single points of failure in protection.
Periodic Testing: Use secondary injection kits and test blocks.
Digital Integration: Utilize SCADA and IEC 61850 IEDs.
Disturbance Recorders (DR/NDR): For event analysis.
Cybersecurity: Implement OT network protection against intrusion.
Prerequisites
•Knowledge in power system components and substation
•Knowledge in power system analysis


