Introduction
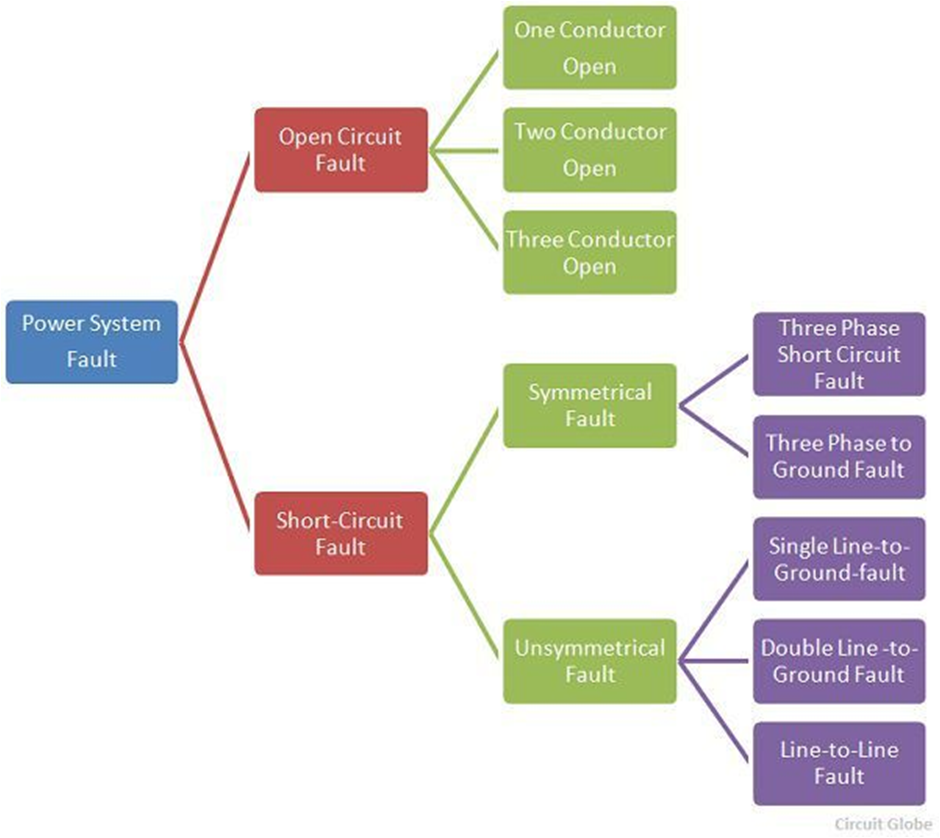
An electrical fault is an abnormal condition, caused by equipment failures such as transformers and rotating machines, human errors, and environmental conditions.
An electrical fault is the deviation of voltages and currents from nominal values or states. Under normal operating conditions, power system equipment or lines carry normal voltages and currents which results in a safer operation of the system. But when fault occurs, it causes excessively high currents to flow which causes the damage to equipments and devices.



Causes of electrical faults in transformer
Causes of electrical faults in transformers can vary depending on various factors, such as the type of transformer, its design, age, operating conditions, and maintenance practices. Some common causes of electrical faults in transformers include:
- Insulation breakdown: Insulation breakdown can occur due to factors such as aging, thermal stress, electrical stress, mechanical stress, or environmental factors. It can result in short circuits, arcing, and other electrical faults in the transformer.
- Overloading: Overloading of transformers beyond their rated capacity can cause excessive heating, and insulation degradation, and ultimately lead to electrical faults. Overloading can occur due to increased load demand, incorrect transformer sizing, or improper load management.
- Voltage surges: Voltage surges, such as lightning strikes, switching surges, or transient overvoltages, can cause insulation breakdown, winding insulation stress, and other electrical faults in the transformer.
- Moisture ingress: Moisture ingress into the transformer can cause insulation deterioration, reduced dielectric strength, and increased risk of electrical faults. Moisture can enter the transformer through various means, such as leaking gaskets, faulty seals, or improper storage and handling.
- Contamination: Contamination of the transformer oil or solid insulation with pollutants, dirt, or conductive particles can lead to increased conductivity, reduced dielectric strength, and increased risk of electrical faults.
- Poor maintenance: Inadequate or improper maintenance practices, such as lack of regular inspection, testing, and servicing, can lead to electrical faults in transformers. This can include neglecting to check oil levels, improper tightening of connections, or failure to detect and address early warning signs of potential faults.
- Age and wear: Transformers have a limited lifespan, and as they age, the risk of electrical faults increases. Winding insulation, bushings, tap changers, and other components can degrade over time due to normal wear and tear, leading to electrical faults.
Prevention of electrical faults in transformers
- Regular maintenance: Regular inspection, testing, and servicing of transformers according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and industry standards can help detect and address potential faults before they escalate.
- Proper loading: Ensuring that transformers are operated within their rated capacity and load management practices are followed to avoid overloading.
- Surge protection: Installing surge protection devices, such as lightning arresters and surge arresters, to protect transformers from voltage surges.
- Moisture control: Proper storage, handling, and sealing of transformers to prevent moisture ingress, as well as regular monitoring of moisture levels in the transformer oil and insulation.
- Contamination control: Monitoring and managing the condition of transformer oil and solid insulation to prevent contamination.
- Early fault detection: Using diagnostic tools and techniques, such as dissolved gas analysis (DGA), partial discharge monitoring, and thermography, to detect early warning signs of potential electrical faults and take timely corrective actions.
- Proper training and skilled personnel: Ensuring that personnel involved in transformer maintenance and operation are trained, qualified, and follow proper procedures to minimize the risk of electrical faults.
Summary
By implementing these preventive measures, it is possible to reduce the risk of electrical faults in transformers, ensure their reliable operation, and extend their lifespan. Regular monitoring, timely maintenance, and adherence to industry best practices are essential to prevent electrical faults and ensure the safe and efficient operation of transformers.


