Objectives
- Define distribution line faults and their significance in electrical distribution systems.
- Understand the impact of faults on system reliability, safety, and service interruptions.
Fault analysis is conducted by DISCOM Engineers for the following purposes
- Locate faults
- Know the cause,
- Determine if protective equipment is operated properly,
- Methods to implement in order to prevent the fault from occurring in the future
Faults are abnormal states of the distribution network, usually associated with open circuits or short circuits or insulation breakdown between two or more points.It can be either temporary or permanent.
The temporary faults include the insulation breakdown by the interaction between the components and external agents (lightning strikes, wind, transient tree contacts, etc.) for a short period of time.
Examples of permanent faults are insulator damage by flashover, underground cable breakdown, and surge arrester damage.

| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Open Circuit Fault | One or more phases are disconnected, usually due to a broken conductor. |
| Short Circuit Fault | Two or more conductors come into contact, causing a high current flow. |
| Ground Fault | A live conductor touches the earth or grounded object. |
| Arc Fault | An electric arc forms due to damaged insulation or loose connections. |

| Type | Description |
|---|---|
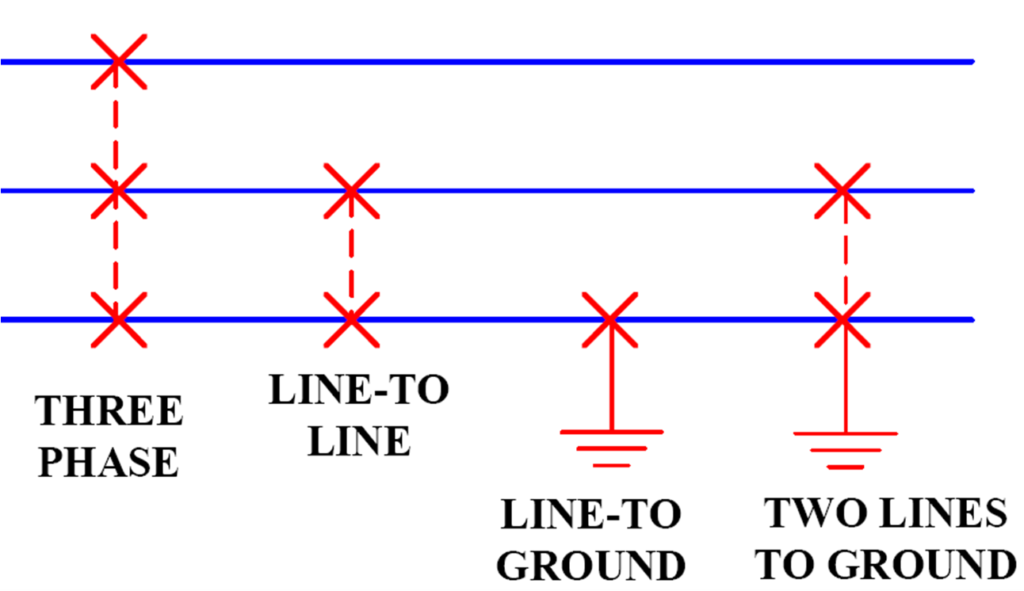
| Single Line-to-Ground (SLG) | One phase touches the ground (most common fault). |
| Line-to-Line (LL) | Two phases touch each other. |
| Double Line-to-Ground (DLG) | Two phases touch the ground. |
| Three-Phase Fault (LLL or LLLG) | All three phases shorted together or to the ground (severe). |

| FAULTS IN OVERHEAD DISTRIBUTION LINE | FAULTS IN UG CABLE | |
| OCCURRENCE | Frequent | Rare |
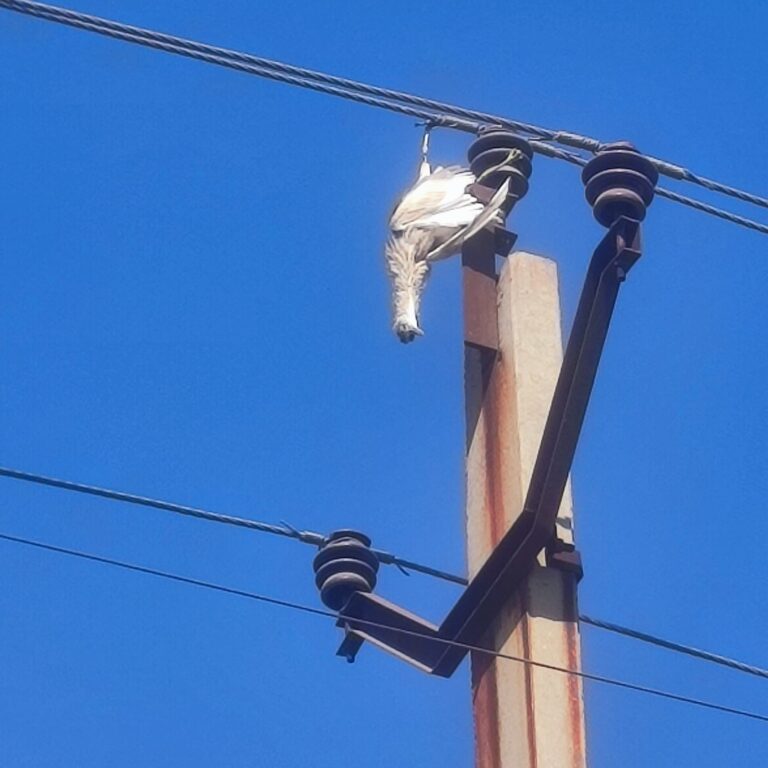
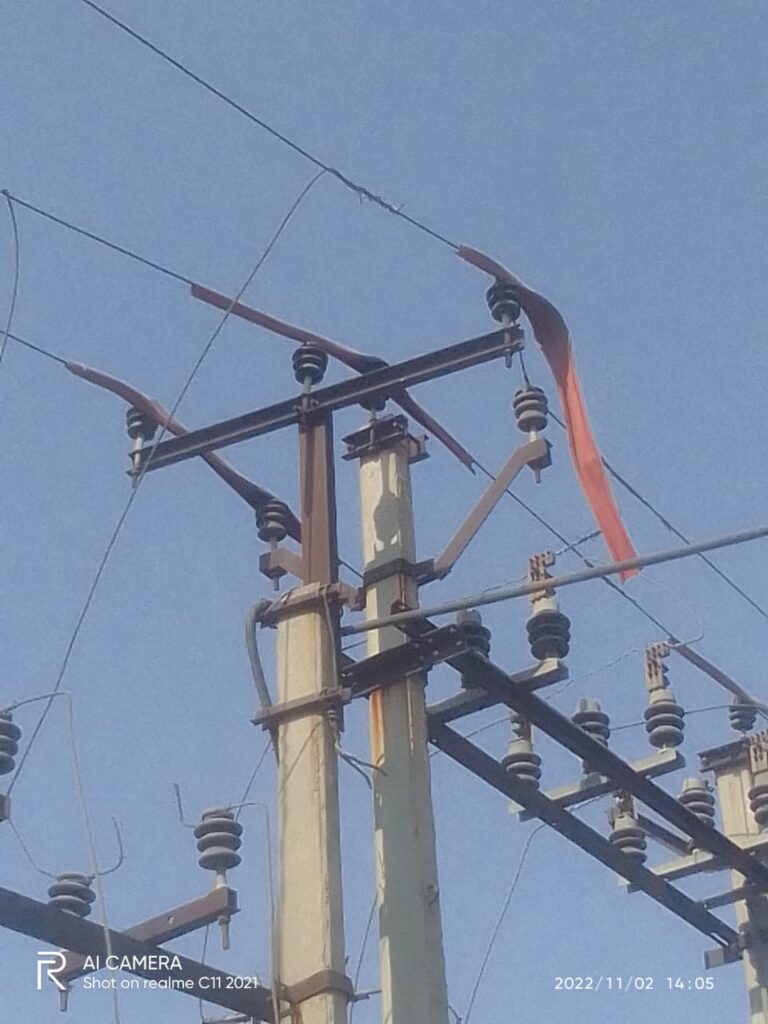
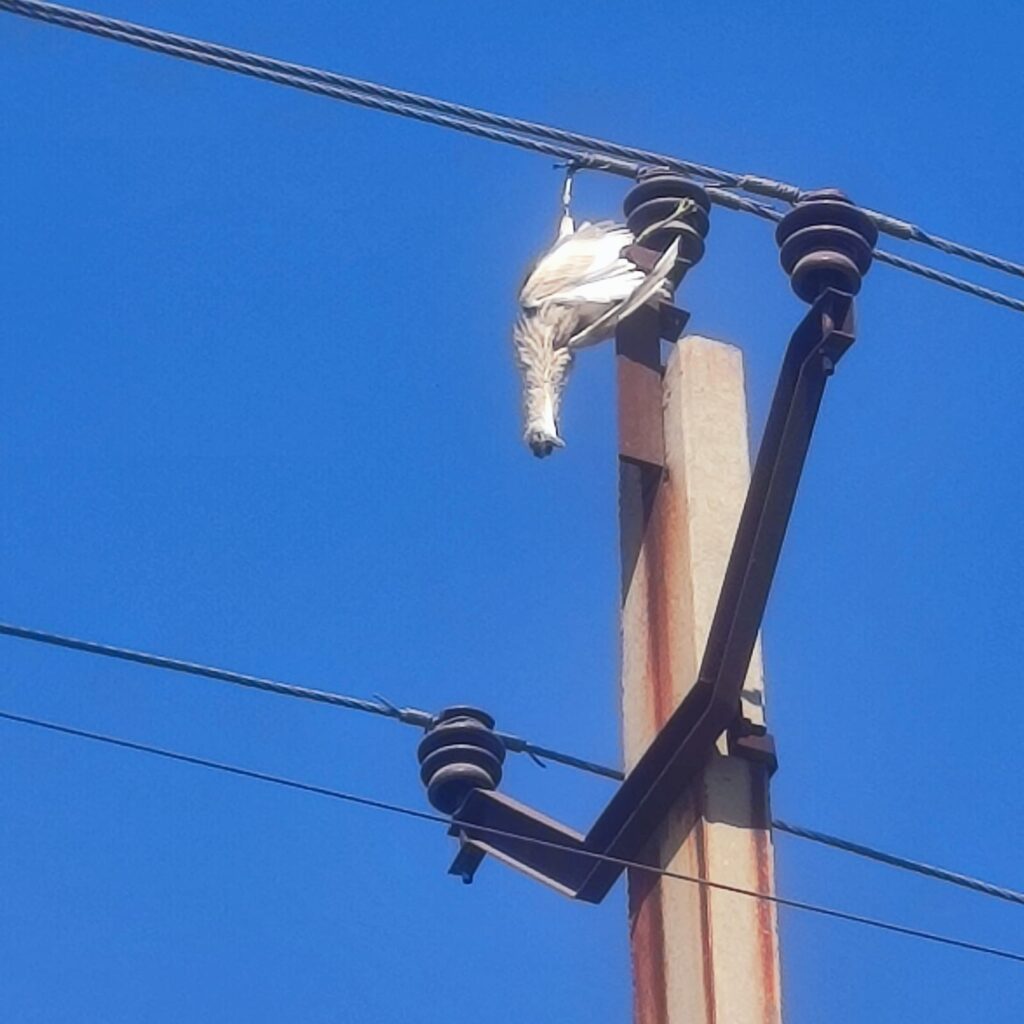
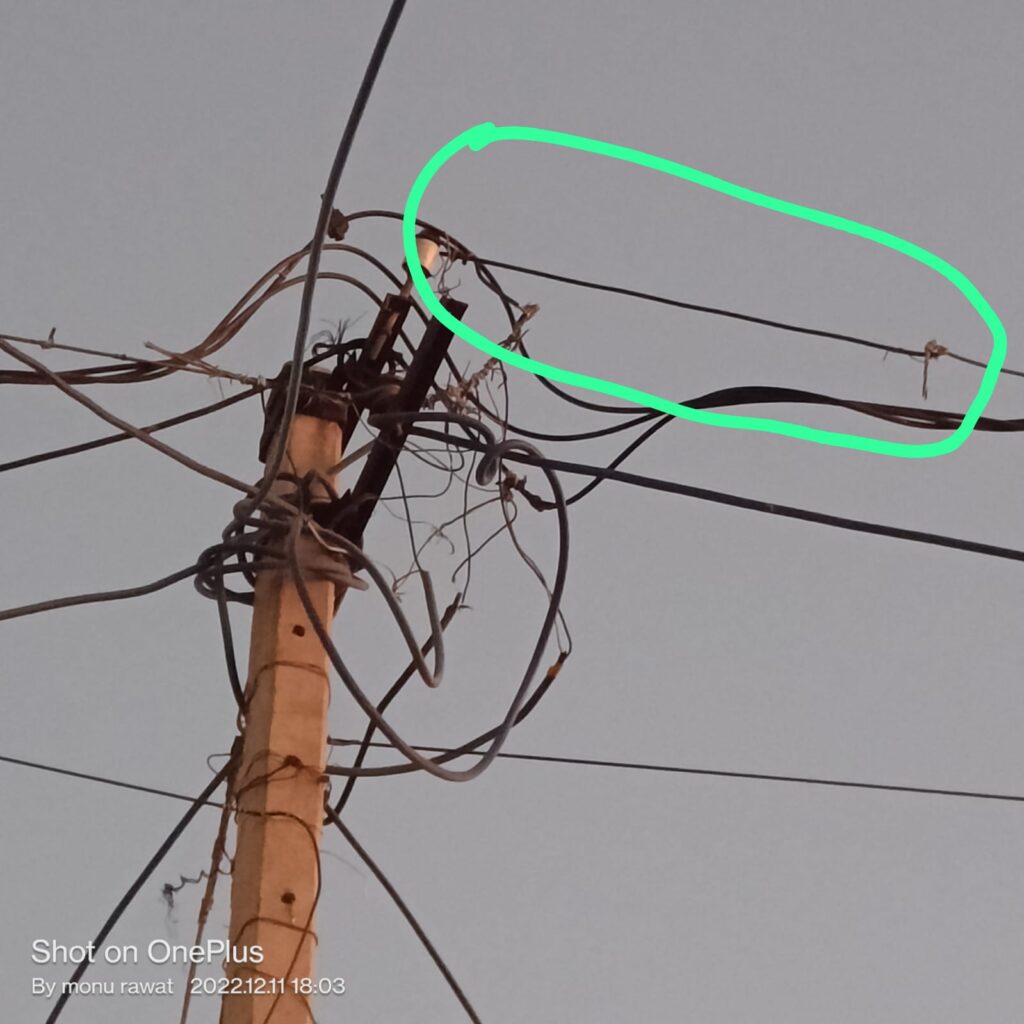
| CAUSES | Extreme Weather Conditions, Tree Branches, Bird Faults, construction, and vehicle, Insulation Puncture, Conductor Snapping | excavator digging, Partial Discharge |
| Fault Rectification | Less time compared to UG Cable | More time |
Effect of Fault
- Danger to Operating Personnel
- Loss of Equipment
- Disturbance in the Interconnected Active Circuits
- Electrical Fire
🛡️ General Fault Mitigation Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| SCADA & Remote Monitoring | Enables real-time fault detection and localization |
| Line Fault Indicators (LFI) | Used on poles to visually show fault presence |
| Preventive Maintenance | Includes insulator washing, vegetation control, etc. |
| Automated Reclosers | Temporarily restore supply after transient faults |
| Proper Earthing | Reduces fault current path resistance |
📘 Standards and Best Practices
- IEEE Std 242 (Buff Book) – Protection and coordination of industrial systems
- IEC 60909 – Short-circuit current calculations
- NESC & NEC – Construction and safety standards
I hope that you got to know about the different types of faults in distribution systems. Thank you for your valuable time spent on the article. Furthermore, please write your feedback in the comment section below related to the power system.


