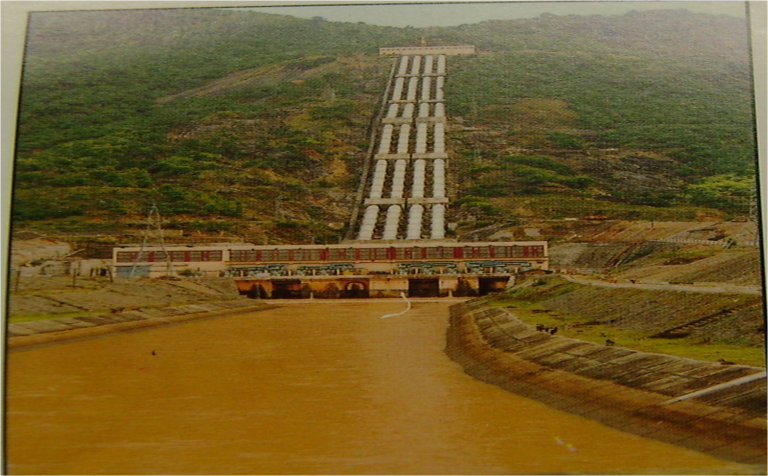
Hydropower Stations are used as a piece of machinery that directly converts the hydraulic power in a waterfall
to mechanical power on the machine shaft. In a hydroelectric power station, a water head is created by constructing a dam across a river or lake. From the Dam, water is led to a water turbine. The water turbine captures the energy in the following water and changes the hydraulic energy i.e. product of the head and flow of water, into mechanical energy at the turbine shaft. The turbine drives the alternator which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.

SITE SELECTION OF POWERHOUSE FOR HYDROPOWER STATION
1. UNDERGROUND POWERHOUSE AND UNDERGROUND TUNNEL.
2. SURFACE POWERHOUSE WITH PENSTOCK IN TUNNEL.
3. SURFACE POWERHOUSE WITH PENSTOCK ON THE SURFACE.
4. SURFACE POWERHOUSE WITH PENSTOCK BURIED 3.0 METERS BELOW THE NATURAL SOIL.
5. SURFACE POWERHOUSE WITH PENSTOCK BURIED AT ROCK LEVEL.
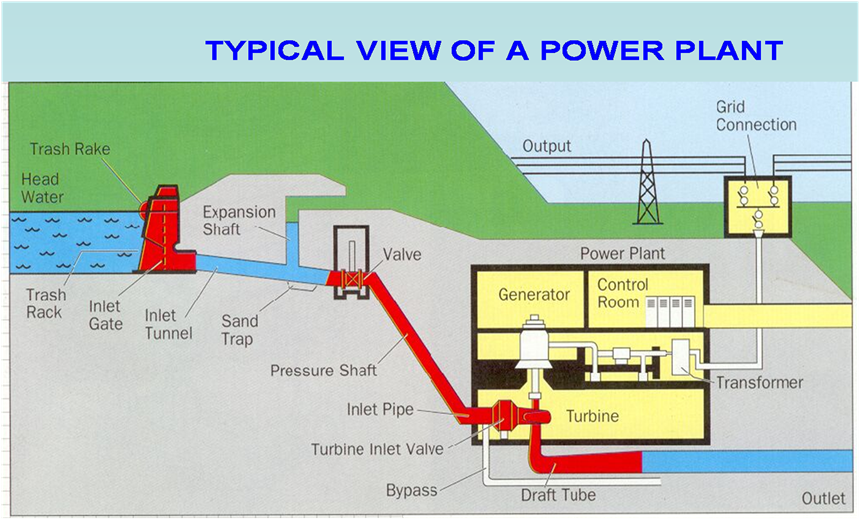
Here is an overview of the key components and the functioning of a typical hydropower station:
Reservoir:
The whole of the water available from the catchment area is collected in a reservoir behind the dam. The purpose of storing of water in the reservoir is to get a uniform power output throughout the year. A reservoir
can be either natural or artificial. A natural reservoir is a lake in high mountains and an artificial reservoir is made by constructing a dam across the river.
Dam:
The water intake is normally constructed in connection with an accumulation dam.
A dam is built across a river for two functions: to impound the river water for storage and to create the head of water. Dams may be classified according to their structural materials such as Timber, steel, earth, rock-filled and masonry.
Surge Tank
A SURGE TANK is a small reservoir or tank (open at the top) in which the water level rises or falls to reduce the pressure swings in the conduit.A surge tank is located near the beginning of the conduit. When the load on the turbine increases, additional water is drawn from the surge tank to meet the increased load requirement. Hence,a surge tank overcomes the abnormal pressure in the conduit when the load on the turbine falls and acts as a reservoir during the increase of load on the turbine.
Penstock:A penstock is a large pipe or conduit that carries water from the reservoir to the turbine. The pressure of the falling or flowing water in the penstock is used to turn the turbine blades and generate mechanical energy.
Turbine: The turbine is a critical component of a hydro power station. It is positioned at the end of the penstock and immersed in the flowing water. The kinetic energy of the water is transferred to the turbine, causing it to rotate. Various types of turbines, such as Francis, Pelton, and Kaplan turbines, are used, with each being suitable for specific conditions and water flow rates.
Generator: Connected to the turbine, the generator converts the mechanical energy from the rotating turbine into electrical energy. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a coil of wire spins within a magnetic field, generating an electric current. The generator typically produces alternating current (AC) electricity.
Transformer:The electricity generated by the generator is often at a relatively low voltage. Transformers are used to step up the voltage to levels suitable for efficient long-distance transmission.
Control Room: Hydro power stations have control rooms staffed by operators who monitor and control the operation of the entire facility. They adjust the flow of water, regulate the generator, and ensure the station operates efficiently and safely.
Tailrace: After the water has passed through the turbine, it exits the power station through a tailrace and is returned to the river downstream. Care is taken to ensure that the discharged water has minimal environmental impact and maintains water quality.
Limitations
The initial Construction Cost is very high.
Summary
Hydropower stations vary in size, from small, run-of-river installations that divert a portion of a river’s flow to large-scale dams that create vast reservoirs. The choice of technology and scale depends on factors such as the available water resources, geography, environmental considerations, and energy demand. Hydropower is a reliable and renewable source of energy, providing a significant portion of the world’s electricity supply.


