Digital Substations:
Manual systems are very hard to troubleshoot and rectify when some interruptions occur while also being tedious to operate. The modern digital substation has the flexibility of data logging over a very long period, and continuous real-time monitoring makes it easier to rectify any problem immediately.
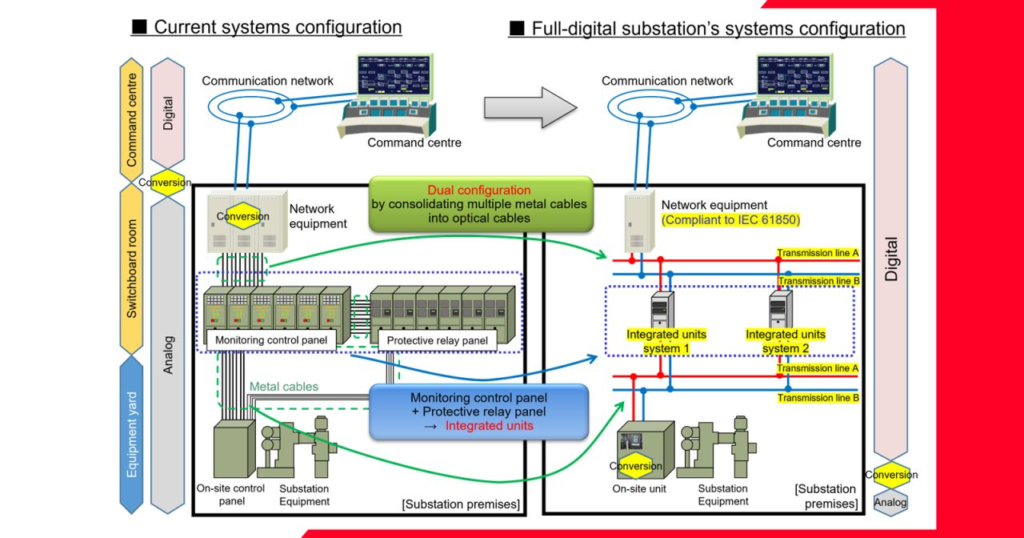
Older substations perform their primary functions but lack digital features like real-time monitoring, data logging, and automation. Upgrading the old control network into a digital network revives the whole substation.
- Key Drivers: Increasing demand for real-time data, grid automation, and remote monitoring.
- Benefits: Improved reliability, reduced maintenance costs, enhanced safety, and better asset management.
- Use Cases: Digital substations use sensors, communication networks, and advanced analytics to monitor equipment health and performance, enabling predictive maintenance and fault detection.
Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs):
- Key Drivers: Need for synchronized measurements for grid stability and reliability.
- Benefits: Real-time monitoring and control of grid conditions, better situational awareness, and enhanced grid stability.
- Use Cases: PMUs provide synchronized data on voltage and current phasors, helping grid operators identify disturbances and make rapid corrective actions.

GIS (Gas-Insulated Substations):
- Key Drivers: Limited space availability in urban areas and improved environmental performance.
- Benefits: Compact design, reduced land requirements, lower maintenance, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Use Cases: GIS technology is commonly used in densely populated areas to minimize the physical footprint of substations while maintaining high voltage capacity.
HVDC (High-Voltage Direct Current):
- Key Drivers: Long-distance power transmission, integration of renewable energy sources, and interconnections between grids.
- Benefits: Lower transmission losses, improved grid stability, and efficient integration of renewable energy.
- Use Cases: HVDC technology is used for transmitting electricity over long distances, often under the sea (submarine cables), and for connecting asynchronous AC grids.
Advanced Sensors and IoT:
- Key Drivers: Increasing focus on data-driven decision-making and predictive maintenance.
- Benefits: Real-time monitoring of equipment health, reduced downtime, and improved maintenance strategies.
- Use Cases: Using sensors to monitor transformer conditions, circuit breakers, and other substation components, providing early warning of potential issues.

What has been the utility experience in the adoption of technologies?
Utility experiences in the adoption of these technologies vary depending on factors such as geographic location, regulatory environment, and specific grid challenges. However, many utilities have reported positive outcomes, including improved grid reliability, reduced operational costs, and better integration of renewable energy sources.
Summary
It’s essential to stay updated with the latest developments in this field, as the adoption of emerging technologies in high-voltage substations continues to evolve to meet the changing demands of the energy sector. Consulting industry reports, attending conferences, and engaging with industry experts can help you gain insights into the most recent developments and utility experiences in technology adoption.


