Current transformers play an important role in measuring electric current in our electric substations. To ensure their proper functioning, we need to perform proper testing on them as a knee point test. In this article, we are going to discuss a knee point test value test of a current transformer and how to perform this test.
Knee Point Test in a Current Transformer
We have studied the functioning of current transformers as they help us to measure electric current by dividing input value by a specific CT ratio. Knee point voltage is the voltage of secondary winding in a current transformer. At the knee point, our CT will be in a saturation state (no change in flux further) due to a higher primary current. We can say, that at this saturation point, there will be no change in secondary current due to the maximum flux in the secondary core.
We need the following key components before starting the test:
- 0 to 230V VARIAC called variable transformer (these transformers help us to change the voltage with the help of a knob by caging tapping in winding).
- Voltage Transformer 230/2000V (Step-up transformer)
- Extension wire.
- Clip on meter.
- Volt Meter/Multi Meter (to measure voltages)
These are required elements that we need before starting testing.
Why do we need Knee Point in CT?
We used PS Core CT for special protection like differential relays, distance relays, HT motors, and generators. Now if the voltage in the secondary increases by knee point voltage then, secondary winding does not feed accurate current as starts misbehaving with its current value with protection devices to which CT is connected.
We can understand this by the following graph:
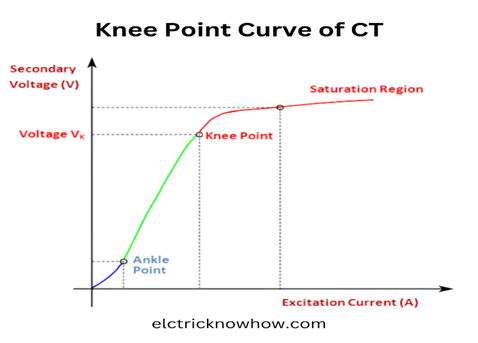
You can see in this graph, we have excitation current on the horizontal axis and secondary voltages on the vertical axis. We apply voltage at the secondary and then there will be a point where the excitation current starts increasing beyond its limit. That point of maximum current gives us the knee point voltage.
Ankle point at the start of the graph is used for the metering coil in CT.
CT Specifications
We need to study the nameplate of specific CT before starting the test. Here is an image representing the CT properties. Let’s read that first:
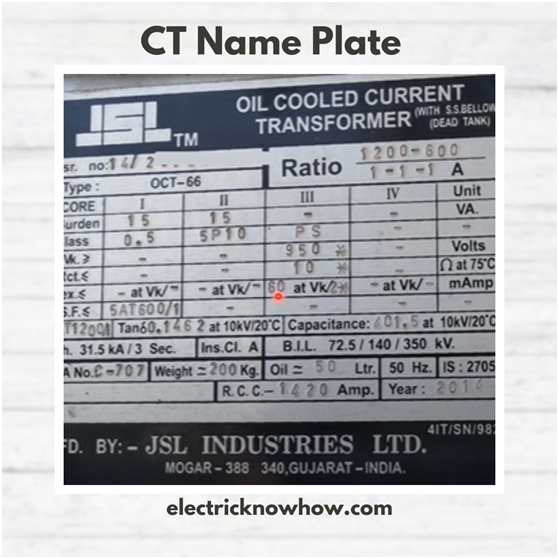
Here are the following things:
Vk = Knee Voltage Point = 950 volts
Iex = Excitation Curret = 60mA at Vk/2
These values are specific to this CT. It means that at the knee point voltage, the excitation current should not be more than 60mA.
How Knee Voltage Occurs?
As we know CT secondary is short, so how the secondary voltages are produced in the secondary of CT? The relay will be connected with the secondary and the relay will provide resistance with the leads/wires connected to the secondary. Core has also resistance when the current passes through the secondary (inducing in secondary with the help of primary current), a voltage will be produced. This voltage should not exceed tan knee point. In case of exceeding this voltage than knee point, the core will be saturated. After that, there will be mutual induction to transfer electric current from primary to secondary. You can see the CT diagram in the following image:
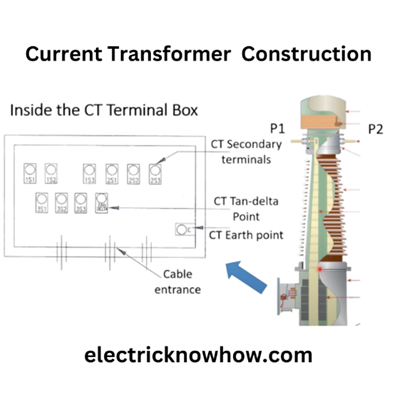
Here are the primary (on the top side) and secondary side (in CT terminal box) with earth point.
Knee Point Procedure
Here is the procedure for the knee point voltage test:
- First, we will make connections.
- VARIAC output will go into the voltage transformer input.
- The output of the voltage transformer will go in PS1 and PS3 in the terminal box of CT.
- We will use a multimeter
Basic Precautions of Testing:
Before testing the CT, you should verify the following conditions.
- Breaker is in an off-state
- Both isolators of CT are in open condition.
- Secondary wires should be removed from the CT terminal box (from the ground).
- We will use a clip-on meter to measure the current in mA and a volt meter to measure the voltage.
- After powering the supply to VARIAC, we will take values at different voltages by turning the knob.
- We will measure current at specific VARIAC voltages.
- We have to take voltage to the knee point by turning the knee of VARIAC.
Test results can be shown in the following table:
| Voltage Value (V) | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 950 | 1100 | 1200 | 1350 |
| Current Value (mA) | 2.5 | 4.5 | 5.7 | 7.2 | 8.7 | 10.3 | 12.3 | 14.5 | 17 | 31 | 55 | 160 |
Where knee point our specific CT is 950 V and saturation current is 60mA. We have checked values 10% more than our knee voltage value. You need to measure the voltage and current by your experiment and CT specifications. You can make a graph using the above current and voltage to check the knee point as we have seen in the previous section of our article.
Conclusion:
We have studied the knee voltage test in the case of the current transformer. These current transformers are important in getting the lower measured values of input current by dividing the incoming value depending on their CT different ratio. So its protection and safety are compulsory. In this article, we have gone through the knee voltage value using VARIAC, voltmeter, and other key components.

